Startup Profit and Loss Statement
$119.00 Original price was: $119.00.$79.00Current price is: $79.00.
34% Off
Get the basics of our Standard Financial Model, with separate sheets for actuals and assumptions. Quickly adapt it to your business and add revenue and expense modeling. Then, visualize key financial metrics with an interactive dashboard!
Description
Managing your startup’s finances can be overwhelming, especially when you’re trying to keep track of multiple revenue streams, expenses, and profits. Without a clear financial picture, it’s easy to make costly mistakes or miss opportunities for growth. Without a proper system in place, it becomes difficult to analyze performance, make informed decisions, and maintain control over cash flow.
That’s where our Startup P&L Statement Template comes in. This customizable template simplifies your financial tracking by offering an organized, easy-to-use structure for tracking income, costs, and profits. It allows you to break down your revenue and expenses in a way that provides immediate insight into your financial performance. With this template, you can identify areas to cut costs, see where your business is making money, and make adjustments to drive growth. Whether you’re a first-time entrepreneur or an experienced founder, this template helps ensure that your financial reports are accurate, up-to-date, and ready for any business decision or investor pitch.
A profit and loss statement (P&L) is a key financial document that shows a business’s revenue, costs, and expenses over a specific period, such as a month, quarter, or year. It’s an essential tool for understanding how well your startup is performing financially. A P&L statement helps summarize your business activities by listing your revenues, subtracting the costs of producing your goods or services, and ultimately showing whether your startup is profitable or operating at a loss.
The P&L statement is often called the income statement or statement of earnings. Regardless of the name, its primary purpose remains the same: to provide insights into your business’s financial health and profitability. By analyzing the P&L, you can assess whether you’re generating enough revenue to cover your expenses and determine areas where improvements can be made.
Purpose of a P&L Statement for Startups
For startups, a profit and loss statement is not just a tool for compliance—it’s an essential resource for decision-making and growth. A well-structured P&L allows you to evaluate your business’s financial trajectory, identify strengths and weaknesses, and stay on top of your financial obligations.
- Helps understand the financial performance: A P&L statement provides a snapshot of how your business is performing in terms of revenue generation and expense management.
- Guides decision-making: It helps you decide where to allocate resources and what adjustments to make to increase profitability.
- Monitors cash flow: By tracking income and expenses, it enables you to predict cash flow and avoid financial bottlenecks.
- Attracts investors and lenders: Investors and creditors require a P&L statement to assess the viability of your startup and its potential for growth and return on investment.
- Tracks business health over time: By regularly updating your P&L statement, you can observe trends in your revenue, expenses, and profits, enabling more informed decision-making.
- Helps with tax compliance: A P&L statement provides the necessary financial data required for tax filings and ensures compliance with local tax laws.
The Importance of a Profit and Loss Statement for Startups
For a startup, financial management is a delicate balancing act. A P&L statement helps make this balance easier by offering an organized way to track and understand where money is coming from and where it’s going. Here’s why it’s so important for startups:
- Helps measure profitability: It’s critical for startups to know whether they’re operating at a profit or a loss. A P&L statement gives you a clear picture of your profitability after accounting for all revenue and expenses.
- Enables effective financial planning: With accurate financial data, you can set realistic goals, create budgets, and forecast future performance with greater accuracy.
- Improves cost control: By detailing your expenses, it’s easier to identify areas where costs can be reduced, which is particularly vital for startups working with limited funds.
- Strengthens investor confidence: A well-maintained P&L statement shows potential investors that you have a firm grasp of your financial situation and are making sound business decisions.
- Improves operational efficiency: Understanding where you’re making or losing money can lead to operational improvements, from renegotiating supplier contracts to adjusting your pricing strategy.
A P&L statement is more than just a financial formality; it is a comprehensive tool for tracking the pulse of your startup, helping you adapt to changing market conditions and make adjustments to boost your bottom line.
How a P&L Statement Helps in Tracking Business Performance and Making Informed Decisions
One of the most valuable functions of a P&L statement is that it helps track your business’s financial performance. For a startup, where every penny matters, understanding how well you’re doing is crucial. A P&L statement allows you to see if you’re hitting your financial targets, if you need to tighten your spending, or if you’re well-positioned to expand.
- Identifies profitability trends: The P&L statement helps you spot patterns in your income and expenses, giving you a clearer view of your financial health over time.
- Assesses business growth: By comparing P&L statements over different periods (monthly, quarterly, or yearly), you can measure whether your revenue is increasing, expenses are under control, and profits are growing.
- Informs pricing and cost strategies: Knowing how much it costs to produce and deliver your product or service helps you adjust prices, cut unnecessary costs, and maintain or improve margins.
- Supports budgeting and forecasting: When making financial forecasts, the P&L statement serves as a guide. You can use it to estimate future expenses, predict revenue, and allocate funds effectively.
When making decisions, having the most accurate, up-to-date financial data is critical. The P&L statement is the foundation upon which you can base your decisions about pricing, expansion, cost-cutting, and more.
Key Elements of a P&L Statement
A profit and loss statement contains several key components that provide a comprehensive overview of your business’s financial health. Each part of the P&L provides different insights, and together they paint a full picture of your startup’s performance.
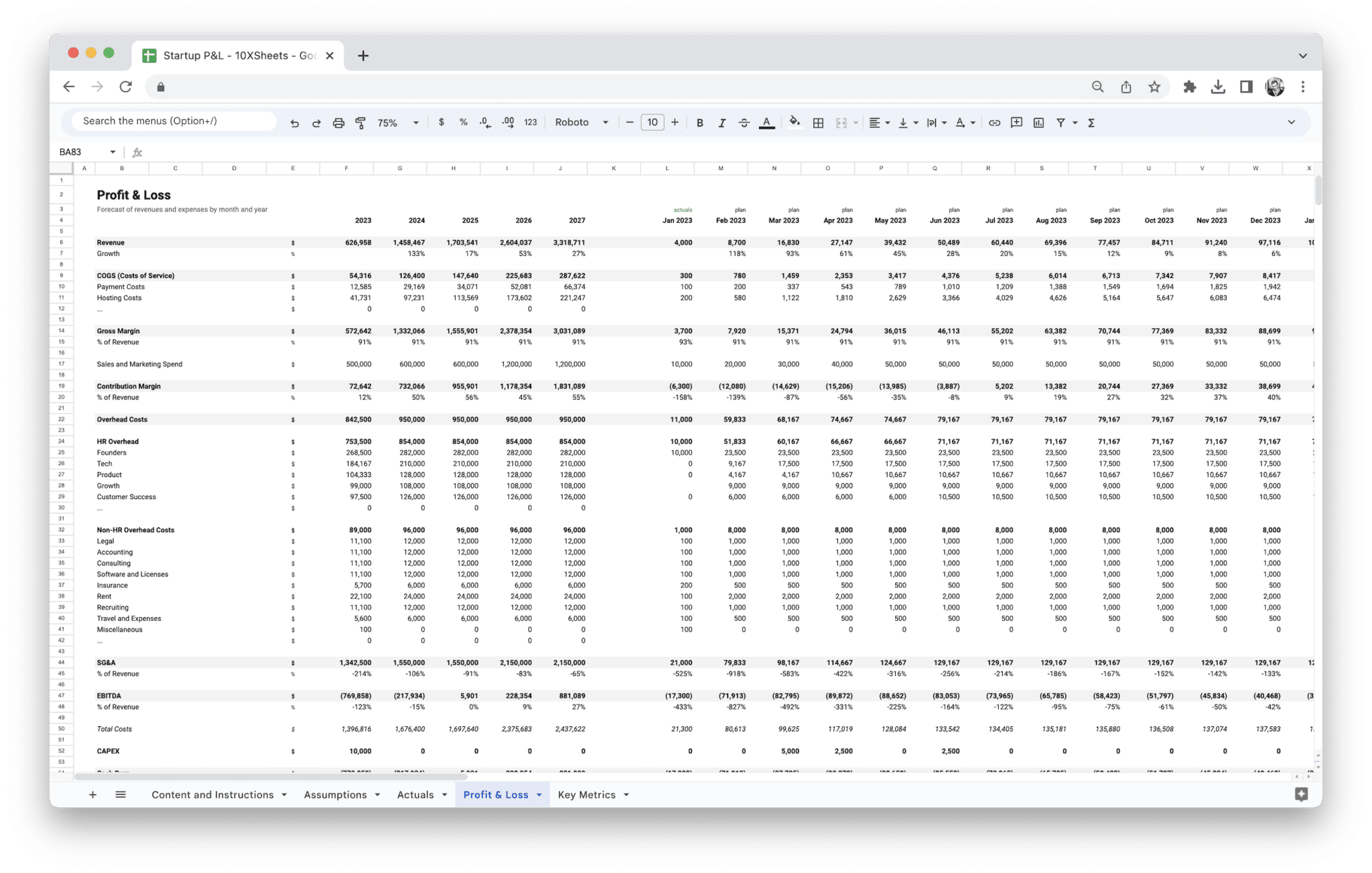
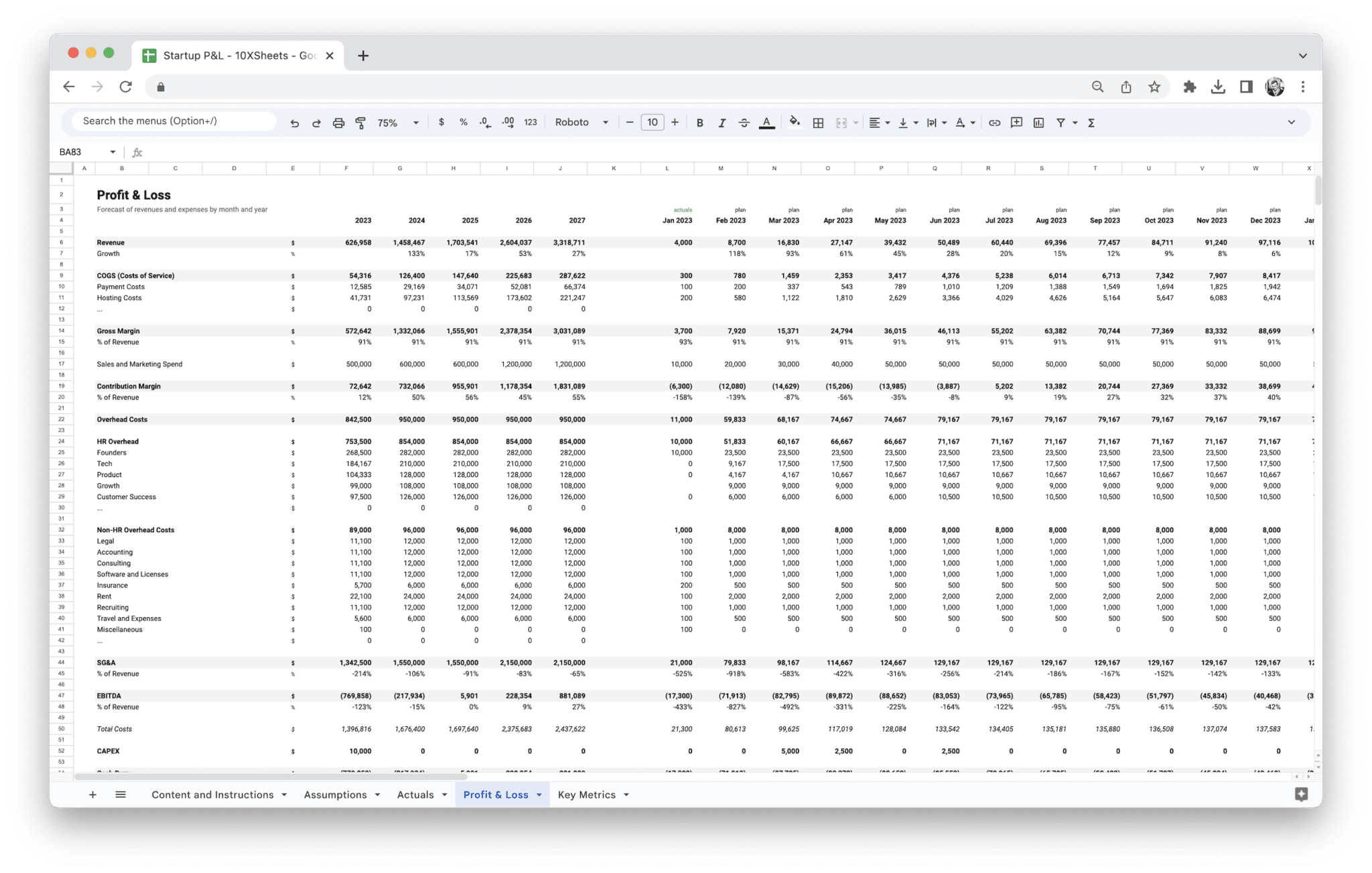
- Revenue: This is the total income from your business’s activities before any expenses are subtracted. It’s often referred to as “top-line” revenue, and it’s important to track how much money is coming in from different sources (product sales, services, etc.).
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): This includes the direct costs tied to the production of goods or services. For product-based businesses, COGS typically includes the costs of raw materials and labor. For service businesses, it might include costs such as contractor fees or software tools.
- Gross Profit: Calculated by subtracting COGS from total revenue. Gross profit gives you a sense of how much money you’re making from the core operations of your business before considering other costs.
- Operating Expenses: These are the ongoing costs necessary to run the business, such as rent, utilities, salaries, marketing, and insurance. Operating expenses are deducted from gross profit to determine operating income.
- Operating Income: The amount left over after subtracting operating expenses from gross profit. This figure shows how much your startup is earning from its primary business operations.
- Net Profit: This is the final figure on the P&L statement, representing the company’s overall profit after all expenses, including interest and taxes, have been deducted. This is often referred to as the “bottom line.”
Understanding each of these components will help you better analyze your business’s finances and make data-driven decisions.
Difference Between a P&L Statement and Other Financial Reports Like Balance Sheets
While a P&L statement is crucial for tracking profitability, it’s just one piece of the financial picture. Other financial reports, such as the balance sheet and cash flow statement, provide additional insights into your startup’s financial condition.
- Balance Sheet: The balance sheet provides a snapshot of your startup’s financial position at a specific point in time. Unlike the P&L statement, which covers a period, the balance sheet lists assets, liabilities, and equity to show your startup’s net worth. It provides insight into how your assets (such as cash and inventory) are funded—whether through debt or equity. While the P&L shows your profitability, the balance sheet highlights your overall financial stability.
- Cash Flow Statement: This report tracks the movement of cash in and out of your business, providing insight into your liquidity and cash management. The cash flow statement focuses on how your startup generates and uses cash, helping you assess whether your business can cover short-term obligations and sustain operations. It complements the P&L by showing where cash is coming from (operating activities, investments, or financing) and where it’s going (capital expenditures, debt repayments, etc.).
In short, the P&L statement focuses on profitability over a period, while the balance sheet shows financial stability at a specific moment, and the cash flow statement focuses on liquidity and cash management. Together, these reports provide a full financial picture, helping you understand not just if you’re making money, but also how well you can manage your assets and obligations.
A profit and loss statement (P&L) is an indispensable tool for any business, especially for startups. If you’re navigating the early stages of a startup, having a clear understanding of your financial performance is crucial. It helps you assess whether your business is on track, allows you to identify issues early on, and ensures that you are making informed, data-driven decisions to fuel your growth.
Importance of a P&L Statement in Financial Forecasting
Financial forecasting is all about predicting your startup’s future revenue, costs, and profit margins based on your current financial data. A P&L statement is central to this process because it provides the most up-to-date information on your income and expenses. With this clear snapshot of your finances, you can estimate how much revenue you’ll likely bring in and how much it will cost you to operate.
By analyzing trends in your P&L, you can forecast future cash flow, identify potential periods of financial strain, and make decisions about where to allocate resources. For example, if your P&L shows a consistent increase in operating expenses, it might indicate a need to re-evaluate where your funds are going and adjust your business model to maintain profitability. This can help you anticipate challenges like cash flow shortages or growing costs before they become urgent issues.
Furthermore, a well-maintained P&L allows you to build more accurate, reliable forecasts, which in turn strengthens your decision-making process. This forward-looking approach is vital for your startup’s sustainability and scalability, as it gives you the data needed to plan your next moves effectively.
Role in Attracting Investors and Securing Funding
If you’re looking to secure investment or funding for your startup, one of the first things potential investors will want to see is your P&L statement. Investors want assurance that your business has a clear, organized understanding of its financial situation. A solid P&L statement provides this assurance by showing your business’s revenue growth, expenses, and net profit over time.
For early-stage startups, securing funding often hinges on demonstrating your financial viability and growth potential. By showing that you have a profitable business model, a reliable revenue stream, and an understanding of your costs, you can increase investor confidence in your startup’s future. A well-organized P&L statement is often the first step in building that trust. Investors will use it to gauge:
- Revenue growth: How much your revenue is growing (or shrinking) over time.
- Profitability: Are you currently profitable, or are you burning cash with a clear path to profitability?
- Cost control: How well you are managing costs and maximizing profitability.
- Financial health: What is the overall state of your finances?
By maintaining accurate financial records and providing investors with a clear picture of your finances, you’ll also demonstrate your professionalism and commitment to transparency—traits that investors highly value.
How a P&L Statement Can Help in Tax Reporting and Compliance
For a startup, managing taxes can be complicated, especially in the early stages when you’re juggling many responsibilities. However, having an up-to-date P&L statement can significantly simplify this process. Your P&L provides the detailed breakdown of income and expenses that is necessary for accurate tax reporting.
When it’s time to file taxes, your P&L statement shows exactly how much revenue your business has generated, what expenses you’ve incurred, and what profits (or losses) you’ve made during the tax period. This data directly feeds into your tax filings, helping you avoid potential mistakes that could lead to penalties or missed deductions.
Moreover, a detailed P&L statement helps you track deductible business expenses, which could reduce your taxable income and, therefore, your tax burden. It also helps you stay compliant with local and national tax regulations by providing transparent financial records that can be easily shared with tax authorities or auditors.
By keeping your P&L statement up to date, you’re not only ensuring smooth tax reporting but also avoiding potential legal issues related to financial mismanagement. It helps your startup stay on the right side of the law, making your life as an entrepreneur a little easier.
Benefits of Using a Profit and Loss Statement Template
Creating a P&L statement from scratch can be time-consuming, especially if you’re not familiar with financial statements or accounting principles. This is where a profit and loss statement template can be incredibly useful. Templates provide a structured framework for organizing your financial data, ensuring that you include all the essential components without missing anything important.
A good template simplifies the process by offering pre-designed categories for revenue, expenses, and profits, which saves you time and effort. This allows you to focus on entering accurate numbers rather than worrying about formatting or creating the structure yourself. Plus, most templates come with built-in formulas to automatically calculate totals and profits, reducing the risk of human error.
Using a template also ensures consistency in your financial reporting. By following a consistent structure every time you generate your P&L statement, you can easily track and compare your financial performance across different periods. This consistency helps identify trends more effectively and makes it easier to spot issues early on.
For startups that lack a dedicated accounting team or professional accountants, a P&L statement template can be a game-changer. It provides clarity, saves time, and enables you to manage your finances with confidence, even without extensive financial expertise. With the help of templates, your financial statements are ready to present to potential investors, your tax advisors, or simply for internal review.
In addition, templates can be easily adapted to your business’s specific needs, so you don’t need to worry about adapting a one-size-fits-all solution. Customization allows you to align the template with the unique structure of your startup and ensures that all relevant financial details are accounted for.
By utilizing a template, you’re setting yourself up for easier financial tracking, smarter decision-making, and smoother interactions with stakeholders, tax authorities, and investors. All these benefits are critical for keeping your startup on the path to growth and success.
Understanding the key components of your startup’s profit and loss statement (P&L) is crucial for managing your finances effectively. Each section of the P&L provides valuable insight into different aspects of your business’s performance. In this section, we’ll break down each of the essential components and explain how they relate to your startup’s financial health.
Revenue: Understanding Different Sources of Revenue for Startups
Revenue is the lifeblood of any business, and for a startup, it’s especially important to track how much money is coming in and where it’s coming from. Revenue refers to the total amount of money your startup earns from selling its products or services, and it forms the foundation of your P&L statement.
For startups, revenue can come from a variety of sources, and understanding where your income is generated is essential for making strategic decisions. There are typically two broad categories of revenue for startups:
- Sales Revenue: This is the income generated from the core business activity—selling your product or service. If you’re running a product-based startup, this might be the revenue from the sale of goods. For a service-based business, it’s the income from contracts or project fees.
- Non-Operating Revenue: This can include income from activities that aren’t directly related to your main business model. For example, interest earned on savings, income from investments, or one-time revenue from selling assets. While this type of revenue may seem attractive, it’s important to separate it from your main operations when analyzing profitability.
For your startup, breaking down revenue streams will help you understand which areas of your business are performing well and which may need more attention. For example, if you have multiple revenue streams (product sales, subscription fees, and consulting), tracking these separately gives you a clearer picture of which source is the most profitable or growing at the fastest rate.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): What It Includes and How to Calculate It
The cost of goods sold (COGS) represents the direct costs associated with the production of the goods or services your startup sells. These are the expenses that go into creating your product, and they directly impact your gross profit. For example, if you run a clothing brand, your COGS would include the cost of raw materials, manufacturing costs, and direct labor involved in making the clothes.
For service-based businesses, COGS would include expenses like employee salaries or contractor fees directly tied to delivering the service.
Understanding and calculating COGS is essential for startups because it allows you to:
- Assess Profitability: COGS gives you a better understanding of how much it costs to produce or deliver your product or service. By knowing this, you can more accurately determine how much revenue is needed to cover these costs and generate a profit.
- Price Setting: Knowing your COGS helps you set prices that ensure you remain profitable. If your COGS is high, you may need to raise prices or find ways to lower production costs to improve margins.
The formula for calculating COGS is:
COGS = Beginning Inventory + Purchases - Ending Inventory
This simple formula allows you to calculate how much it cost to produce the goods sold during a specific period. If you are tracking your inventory and expenses correctly, COGS should be easy to calculate each period.
Operating Expenses: Types of Expenses and Their Impact on Profitability
Operating expenses are the ongoing costs that are necessary to run your business but aren’t directly tied to producing the goods or services you sell. These costs are necessary for the day-to-day operations of your startup and include items like rent, utilities, marketing, and salaries for non-production staff.
Operating expenses fall into two primary categories:
- Fixed Expenses: These are costs that remain constant regardless of how much revenue your startup generates. Examples include rent, insurance, and salaries for permanent staff. Since fixed expenses don’t fluctuate with sales volume, they can have a significant impact on profitability if not carefully managed.
- Variable Expenses: These expenses change depending on how much you sell. For example, shipping costs, sales commissions, and materials required for production may increase as you sell more products. While variable expenses are more closely linked to sales, they still need to be carefully monitored to maintain profitability.
Operating expenses are essential for understanding how efficiently your startup is being run. If your operating expenses are too high relative to your revenue, your startup could be at risk of losing money even if you’re making a good amount of sales. By tracking these costs and looking for areas to reduce waste or improve efficiency, you can help increase your overall profitability.
Gross Profit: How It Is Calculated and Its Significance
Gross profit is the amount of money left over after subtracting your COGS from your revenue. It reflects the basic profitability of your startup’s core business activities—how much you’re making after paying for the production or delivery of your products or services.
To calculate gross profit, you simply subtract COGS from total revenue:
Gross Profit = Revenue - COGS
Gross profit is a key indicator of the efficiency of your business operations. A high gross profit margin means your startup is making a solid return on sales, while a low gross profit margin might indicate that your COGS are too high, or your prices are too low. For instance, if your gross profit margin is consistently low, you may need to revisit your pricing strategy, renegotiate with suppliers, or find ways to reduce production costs to increase profitability.
Gross profit is also a good indicator of how sustainable your business model is. If you’re generating strong gross profit margins, it suggests that your product or service is scalable, and you can potentially invest in marketing, sales, or other growth activities. If your gross profit margin is weak, however, it could signal that the business model isn’t sustainable long-term unless adjustments are made.
Operating Income: Distinguishing Operating Income from Net Income
Operating income is a measure of your startup’s profitability from core operations, excluding any non-operating income and expenses like interest and taxes. Essentially, it tells you how much profit your business is making after covering both COGS and operating expenses.
The formula for operating income is:
Operating Income = Gross Profit - Operating Expenses
Operating income is critical for understanding how well your startup is managing its operations. While net income is the ultimate indicator of profitability, operating income focuses specifically on your core business activities, excluding factors like taxes, interest, or extraordinary items that may distort the picture.
One important thing to note is that operating income gives a better view of how well your startup is running its day-to-day operations. For example, if your operating income is consistently high, it’s a sign that your business is efficiently converting revenue into profits. If operating income is low or negative, it suggests that the core business activities are not profitable, and you may need to adjust your operational strategy.
Net Profit: What It Means and Why It’s Essential for Startup Growth
Net profit, often referred to as the “bottom line,” is the final measure of your startup’s profitability after all expenses, including operating costs, interest, taxes, and any non-operating items, have been subtracted from your total revenue. This is the amount of money your startup has left after all costs have been accounted for, and it represents the true financial success of your business.
The formula for calculating net profit is:
Net Profit = Operating Income - Other Expenses (Interest, Taxes, Non-Operating Costs)
Net profit is the ultimate measure of your startup’s financial health. If your startup is making a consistent net profit, it indicates that your business is sustainable and can continue to grow. However, if you’re running at a loss or your profits are shrinking, it’s a sign that you need to reevaluate your business strategy.
Net profit is especially important for attracting investors and securing funding. Investors want to see that your startup is not only generating revenue but is also able to manage costs effectively and deliver strong, sustainable profits. For startups, having a clear path to profitability is key to long-term success. Net profit tells you whether that path is clear or if adjustments are needed.
By understanding and tracking each of these components—revenue, COGS, operating expenses, gross profit, operating income, and net profit—you gain a complete picture of your startup’s financial performance. This comprehensive view helps you make informed decisions that can drive growth and improve your startup’s bottom line.
Creating a profit and loss statement (P&L) for your startup might seem overwhelming at first, but it doesn’t have to be. By breaking the process down into clear, manageable steps, you can easily produce an accurate report that gives you valuable insights into your business’s financial performance. A P&L statement is a powerful tool that will help you understand how much money your business is making, where it’s being spent, and whether you’re on track to meet your financial goals.
Filling Out the P&L Statement
The first step in creating your P&L statement is to gather all the necessary data. This includes information about your revenue, expenses, and any other financial transactions that have occurred during the reporting period (whether monthly, quarterly, or annually). You’ll need accurate figures for both income and expenses to ensure that your P&L is a true reflection of your business’s performance.
Step 1: Start with Your Revenue Revenue is the top line of your P&L statement, and it represents the total amount of money your business has earned from selling products or services. Depending on the complexity of your business, revenue may come from various sources, including sales, subscriptions, or one-time fees. For simplicity, list your total revenue for the period you’re reporting on.
- Record gross revenue first: This is your total sales or income before subtracting any expenses or returns.
- Account for returns or discounts: If there were any product returns, refunds, or discounts offered to customers, make sure to subtract them to calculate net revenue.
Step 2: Calculate the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) The next line on your P&L is the cost of goods sold (COGS). This figure includes all the direct costs associated with producing the goods or services you sold. If you’re a product-based business, COGS would include the cost of materials, labor, and manufacturing. For a service-based business, COGS might include contractor fees or employee wages directly tied to delivering the service.
- Direct production costs: Be sure to include everything that is directly related to the creation of your products or services.
- Subtract inventory changes: If your inventory has changed throughout the period, adjust for the beginning and ending inventory to calculate the exact cost of goods sold.
Step 3: Subtract Operating Expenses Operating expenses include all the costs associated with running your business, excluding the direct costs of production. These are the costs that allow your business to function on a day-to-day basis, such as rent, utilities, marketing, and salaries for non-production employees.
- List each expense: Categorize operating expenses into fixed and variable costs. Fixed costs (like rent) will stay the same, regardless of your sales, while variable costs (like marketing or sales commissions) will fluctuate with business activity.
- Be thorough but realistic: Don’t leave anything out. While it’s important to be as accurate as possible, you don’t want to overestimate or forget about minor costs that could add up.
Step 4: Calculate Gross Profit Gross profit is the amount of money you have left after subtracting COGS from your total revenue. It shows you how much profit your startup is generating from its core business activities. This is a crucial number to track, as it indicates the efficiency of your production process.
Formula: Gross Profit = Revenue – COGS.
Step 5: Subtract Other Expenses to Calculate Operating Income Once you’ve calculated your gross profit, the next step is to subtract your operating expenses (like rent, salaries, and utilities). This will give you your operating income, which reflects how much profit you’re making from your core business operations before accounting for any non-operating costs like interest or taxes.
Operating income formula: Operating Income = Gross Profit – Operating Expenses.
Step 6: Deduct Non-Operating Expenses to Find Net Income The final step is to subtract any non-operating expenses, such as interest payments, taxes, or one-time costs (like legal fees or penalties). Once these deductions are made, you’ll be left with your net profit (or net income), which shows your startup’s true profitability for the period.
Net income formula: Net Income = Operating Income – Non-Operating Expenses.
Tips for Accurately Estimating Revenue and Expenses
Accurately estimating revenue and expenses is one of the most important aspects of creating a reliable P&L statement. Here are some tips to help ensure that your numbers are as accurate as possible:
- Use Historical Data: If your startup has been operating for a while, refer to past financial data to project your revenue and expenses. Historical trends are one of the best predictors of future performance. If you’re just starting out, do market research and look at industry benchmarks to estimate revenue and costs.
- Estimate Conservatively: Especially in the early stages of your startup, it’s better to overestimate your expenses and underestimate your revenue. This approach will give you a cushion to cover unexpected costs and give you a more realistic picture of your financial performance.
- Account for Seasonal Variations: If your business experiences fluctuations in sales due to seasonality (e.g., higher sales during holidays), make sure to account for these changes in your projections. Understanding your business cycle is crucial to creating an accurate P&L.
- Factor in Contingencies: Be mindful of unexpected costs, such as equipment repairs, legal fees, or one-time purchases. These may not be part of your regular expenses but can affect your profitability.
- Review Industry Standards: If you’re unsure about what constitutes reasonable costs or expected revenue, review what other businesses in your industry typically report in their P&L statements. This can help you get a clearer idea of what to expect.
Importance of Consistency in Financial Reporting
Consistency is key when it comes to financial reporting. Your P&L statement isn’t just a snapshot of your business’s financial health for a single period; it’s a tool for tracking performance over time. To make meaningful comparisons, your P&L must be consistently organized and formatted in the same way across different periods.
- Regular updates: Update your P&L statement regularly, whether it’s monthly, quarterly, or annually. Consistent updates allow you to monitor trends and address financial issues before they become significant problems.
- Standardized categories: Stick to a consistent set of revenue and expense categories across all your reports. This makes it easier to track your startup’s performance and compare data across different periods. For example, always report rent, salaries, and marketing costs under the same categories so that you can see if these expenses are increasing or decreasing over time.
- Accurate comparisons: Consistency in how you present your P&L statements helps you track growth and identify areas where your business is improving or struggling. If you change the way you categorize expenses or report revenue from one period to the next, it will be difficult to compare the results accurately.
Having a consistent format allows you to create financial reports that make sense to both you and any stakeholders, such as investors or lenders. For example, if you’re showing an investor your P&L statement from last year and this year, they’ll be able to compare the two easily and spot trends or areas that need attention.
Finally, maintaining consistency in your reporting helps you create reliable forecasts. The more accurately and consistently you report your finances, the better you’ll be at predicting your future performance and making informed decisions about where to focus your efforts.
In short, creating a profit and loss statement for your startup is an essential exercise in financial management. It provides a clear snapshot of your business’s financial health, helps you make more informed decisions, and ensures that you’re on track to achieve your goals. By following the steps outlined above, being conservative in your estimates, and maintaining consistency in your reporting, you’ll set your startup up for long-term success.
A profit and loss statement (P&L) template is a powerful tool for startups, making the process of financial reporting much simpler and more efficient. While creating a P&L from scratch can be time-consuming, using a template streamlines the process, ensuring you don’t miss key details and helping you maintain a professional approach to financial tracking. The beauty of a customizable P&L statement template lies in its flexibility—you can tailor it to fit your unique business model while still adhering to sound financial reporting principles. Below, we’ll walk through how to effectively use a P&L template, adjust it for your startup’s needs, and understand how often you should update and review your statement to stay on top of your finances.
Walkthrough of a Customizable P&L Statement Template
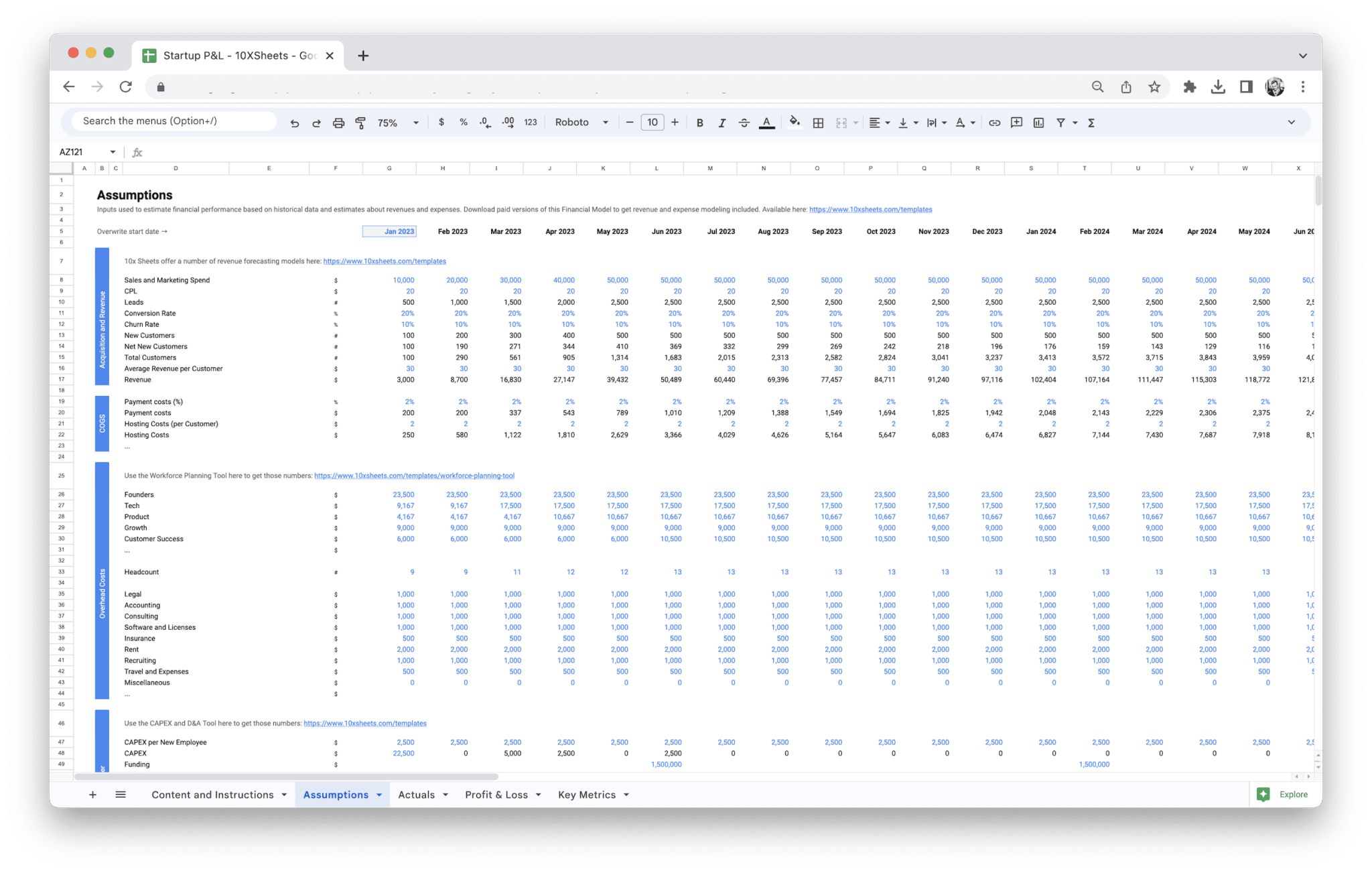
Using a P&L template is an excellent starting point for any startup, especially when you’re just getting the hang of financial reporting. Most templates come with pre-designed categories for revenue, cost of goods sold (COGS), operating expenses, and other key figures, allowing you to input data easily. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how to use a customizable P&L template:
- Download or Choose a Template: You can find free or paid templates online for Excel, Google Sheets, or other financial tools. Choose one that suits your business model. For example, if you’re a subscription-based startup, look for a template that has a section for recurring revenue streams. If you sell physical products, a template with space for inventory tracking might be useful.
- Input Revenue Information: The first section of your template will be dedicated to revenue. Start by entering your total sales or income for the reporting period. Break down your revenue into different streams (product sales, service income, or one-time fees) if applicable. A good template will automatically sum up these figures for you, so you’ll only need to input the specific amounts.
- Enter COGS: Next, you’ll input the cost of goods sold (COGS). The template will have a field for materials, labor, and any other direct costs associated with producing your product or service. This section will help you calculate your gross profit once these costs are subtracted from your revenue. A customizable template should allow you to adjust these categories based on your specific expenses.
- Fill in Operating Expenses: Operating expenses are often the most varied for startups, and a well-designed template will have placeholders for different types of operating costs, such as marketing, rent, utilities, insurance, and salaries. As you enter these figures, the template will calculate your total operating expenses and allow you to assess how these costs compare to your revenue.
- Calculate Profit: After entering your revenue and expenses, the template will automatically calculate your gross profit (revenue minus COGS) and operating income (gross profit minus operating expenses). Finally, once you account for any non-operating expenses (interest, taxes, etc.), the template will provide you with net profit.
The benefit of using a template is that all these calculations are done for you. Instead of spending time manually adding up totals and ensuring everything balances, the template does the hard work while you focus on entering the right numbers.
How to Tailor the Template to Your Startup’s Specific Needs
A P&L template is customizable, which means you can modify it to suit your specific startup’s needs. As your business grows, it’s essential to adapt your template to reflect the changes in your revenue streams, expenses, and overall financial structure. Here’s how you can tailor the template to your business:
- Add or Remove Categories: Depending on your business type, you might need to adjust the default categories in the template. For instance, if you run an e-commerce business, you may want to add a separate category for shipping costs or packaging materials under COGS. If you operate a SaaS (Software as a Service) business, you might need to add a line item for software development or cloud hosting services as part of your operating expenses.
- Break Down Revenue Streams: Many startups have multiple revenue streams, and a good template should allow you to break these out separately. For example, if your startup sells both products and services, you may want to have distinct categories for product revenue, service fees, and any other income (such as investment income or licensing fees). This will give you a clearer picture of where your profits are coming from and allow you to focus your resources on the most profitable areas.
- Customizing Expense Categories: Operating expenses can vary greatly depending on your industry. You may need to add additional expense categories that are relevant to your business. For example, if you’re a tech startup, you might have high costs for R&D (research and development), or if you run a restaurant, you may need to include food and beverage costs, staff tips, or maintenance fees for your equipment. Customizing these categories helps you track the most critical expenses and make decisions accordingly.
- Adjust the Time Frame: Templates often allow you to adjust the time frame, so if you’re reporting on a monthly, quarterly, or yearly basis, you can set it to reflect the reporting period you’re working with. Customizing the time frame will give you a more accurate picture of how your business is performing and will allow for more granular tracking.
- Add Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): As your business grows, you may want to track additional financial KPIs beyond revenue and profit. For example, you could include a section for customer acquisition costs (CAC), lifetime value of customers (LTV), or gross margin percentage. These indicators can provide more insight into how effectively your business is growing and generating value. Many customizable P&L templates have room for these KPIs, or you can add your own.
By tailoring your P&L template to your specific needs, you ensure that you’re tracking the most important financial metrics for your startup. The goal is to have a P&L statement that not only meets standard accounting requirements but also gives you the insight needed to make strategic decisions.
How Often to Update and Review the P&L Statement
Once your P&L template is set up and customized to your needs, the next step is ensuring that you keep it up-to-date. Regular updates and reviews are essential for making sure that your financial tracking remains accurate and relevant. Here’s how often you should update and review your P&L:
- Monthly Updates: For most startups, updating the P&L statement monthly is the best practice. This allows you to track performance on a relatively short-term basis, giving you enough time to spot trends and adjust your strategy if necessary. Monthly updates are especially useful if your business has fluctuating income or if you have variable expenses that could change on a regular basis.
- Quarterly Reviews: While monthly updates are important, quarterly reviews offer a more comprehensive view of your business’s financial health. A quarterly review allows you to analyze patterns, compare data across months, and make strategic adjustments for the upcoming quarter. If you’re seeking investors or trying to secure funding, quarterly P&L reviews will also give them a solid understanding of your financial trajectory.
- Annual Review: An annual review of your P&L is essential for assessing the overall performance of your startup and planning for the year ahead. At the end of the year, you can look back on your financial performance, compare it to the previous year, and set new financial goals. This review is also useful for tax purposes, as you’ll need an accurate, year-end statement for filing your taxes.
- When Seeking Funding or Reporting to Stakeholders: If you’re actively seeking funding or have investors or stakeholders who are involved in the business, you should update your P&L more frequently. In these cases, you might be required to provide monthly or quarterly reports to show investors that you’re on track with your financial goals.
No matter how often you update your P&L, the most important thing is to be consistent. Regular updates ensure that you have an accurate and timely understanding of your financial health. The more you review your P&L, the better equipped you’ll be to make informed decisions about your startup’s future.
By using a customizable P&L statement template and updating it regularly, you will have a reliable tool to manage your startup’s finances. With a clear view of your revenue, expenses, and profits, you can make smarter decisions and adjust your strategies for growth.
As your startup grows, managing your finances becomes increasingly complex. At the early stages, the primary focus may be on getting the business off the ground and ensuring cash flow, but as you scale, strategic financial management becomes essential to ensure sustainable growth and profitability. Here are some advanced tips to help you take your startup’s financial management to the next level:
- Track Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) Beyond Profit: While profitability is important, there are other metrics that can offer critical insight into the health of your startup. Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as customer acquisition cost (CAC), lifetime value of a customer (LTV), and the churn rate are incredibly valuable. By understanding these metrics, you can make better-informed decisions on pricing, marketing, and product development. For example, if you notice that your CAC is increasing without a corresponding increase in LTV, it might signal that you need to rethink your marketing strategies or improve your customer retention efforts.
- Use Cash Flow Projections for Long-Term Planning: Even though profit is a key measure of your business’s success, cash flow is what keeps your startup alive. Use cash flow projections to plan for future financial needs and avoid running out of money. It’s essential to forecast when you might face cash shortfalls and plan your spending accordingly. Cash flow management is especially important for startups that rely on investments or loans to fund their operations. Ensure that you always have enough working capital to cover your day-to-day operations and avoid delays or missed opportunities.
- Embrace Technology for Financial Automation: Financial management doesn’t need to be a time-consuming or error-prone task. There are numerous software tools and apps available that can automate parts of your financial process. Tools like accounting software (QuickBooks, Xero) can help track expenses, categorize transactions, and generate reports automatically, saving you time and reducing human error. Furthermore, automating recurring tasks such as invoicing, payroll, and tax filing can streamline operations and free up resources for other critical areas of your startup.
- Implement Regular Financial Reviews: Just as you conduct quarterly or monthly updates of your profit and loss statement, it’s also important to review your financial performance regularly. A monthly financial review can help you catch any discrepancies early and allow you to make adjustments quickly. In these reviews, focus not just on your P&L, but also on your balance sheet and cash flow statement. Identifying trends and patterns early on can prevent future financial issues, especially in the fast-moving world of startups where market conditions, operational costs, or sales strategies can change rapidly.
- Plan for Tax Efficiency: As a growing startup, tax planning should be an ongoing process, not something that you leave until the end of the year. Tax laws can be complex, but taking steps to reduce your tax burden is essential to ensuring that your business remains profitable. Work with a tax professional to explore tax deductions, credits, and other strategies such as deferring income, setting up retirement plans for employees, or utilizing research and development (R&D) tax credits if applicable. Planning ahead can save you money and ensure that your startup remains in compliance with local tax regulations.
- Diversify Your Funding Sources: As your startup grows, it’s important to explore different ways to finance your operations, especially as relying on a single funding source (such as venture capital or loans) can be risky. Look into alternative financing options like crowdfunding, grants, or strategic partnerships that might be available to your business. Diversifying funding sources helps you avoid financial strain in case one avenue becomes unavailable or more costly. Additionally, using a variety of funding sources can provide more flexibility and lower your overall cost of capital.
- Monitor Your Profit Margins Closely: One of the most critical aspects of financial health is your profit margins. While revenue growth is important, it’s equally vital to ensure that your profit margins remain healthy as you scale. This means closely monitoring both gross margins (revenue minus COGS) and net margins (profit after all expenses). If your margins are shrinking, it may indicate that your business model needs to be adjusted, whether that’s by cutting unnecessary costs, renegotiating supplier contracts, or adjusting your pricing strategy.
Managing your startup’s finances effectively goes beyond just tracking income and expenses—it’s about making strategic decisions that will position your business for long-term success. These advanced tips will help you take control of your financial future, avoid common pitfalls, and foster a strong foundation for growth.
While creating a profit and loss statement may seem straightforward, there are several common mistakes that entrepreneurs and startup founders often make when compiling their financial data. These errors can lead to inaccurate financial reports, poor decision-making, and missed opportunities. Here are some common mistakes to avoid when creating your P&L statement:
- Overestimating Revenue Projections: It’s easy to be overly optimistic about future revenue, especially when you’re just starting out and excited about your product or service. Overestimating revenue can lead to unrealistic expectations and poor budgeting decisions. Always base your projections on historical data, market trends, and realistic assumptions to avoid setting yourself up for disappointment.
- Underestimating Expenses: Startup founders sometimes forget to account for hidden or one-time costs, such as legal fees, unexpected repairs, or new software subscriptions. Underestimating expenses can result in cash flow issues down the road, leaving you unable to cover operational costs. Be thorough in tracking all potential expenses and consider setting aside a buffer for unforeseen costs.
- Failing to Update the P&L Regularly: A P&L statement is only useful if it reflects the current state of your finances. Failing to update your statement regularly—whether monthly, quarterly, or yearly—can lead to outdated information that doesn’t reflect your startup’s actual performance. Regular updates allow you to identify trends, make necessary adjustments, and stay on top of your financial health.
- Mixing Personal and Business Finances: Especially for new founders, it can be tempting to mix personal and business finances, particularly if you’re operating as a sole proprietor or small LLC. This can lead to confusion when tracking revenue and expenses, and it also makes it difficult to assess the financial health of your startup. Always keep personal and business expenses separate, and use accounting tools or dedicated business bank accounts to ensure clarity.
- Not Tracking Non-Operating Expenses: Non-operating expenses, such as interest payments or taxes, are often overlooked when creating a P&L statement. These expenses can have a significant impact on your net profit and should not be ignored. Make sure your P&L statement accounts for all financial obligations, both operating and non-operating, to get an accurate view of your startup’s profitability.
- Ignoring Seasonal Variations: Many startups experience seasonal fluctuations in revenue and expenses. For example, an e-commerce business may see higher sales around the holidays, or a seasonal service provider may experience spikes in demand during the summer months. Ignoring these fluctuations when creating your P&L can lead to unrealistic financial expectations and cash flow issues. Be sure to account for seasonality in your forecasting and expense tracking.
- Not Being Detailed Enough with Expense Categories: A vague or overly simplified P&L can make it difficult to identify specific areas of inefficiency or financial strain. For example, lumping all expenses into a single category for “operating expenses” doesn’t provide enough insight into where money is being spent. Break down your expenses into more detailed categories to get a clearer understanding of where costs are rising or where savings can be made.
- Failing to Account for Depreciation and Amortization: Many entrepreneurs neglect to factor in depreciation or amortization when calculating their expenses. These are non-cash expenses that reflect the reduction in value of assets like equipment, machinery, or intellectual property over time. Ignoring them can result in an inaccurate representation of your startup’s financial condition. Make sure to account for depreciation and amortization to provide a more accurate P&L.
Avoiding these common mistakes is critical for maintaining accurate financial reporting and making informed decisions about your startup’s future. By staying diligent and cautious, you’ll be able to create a P&L statement that truly reflects your startup’s financial health, leading to more strategic decision-making and greater long-term success.
Get Started With the Startup P&L Statement!
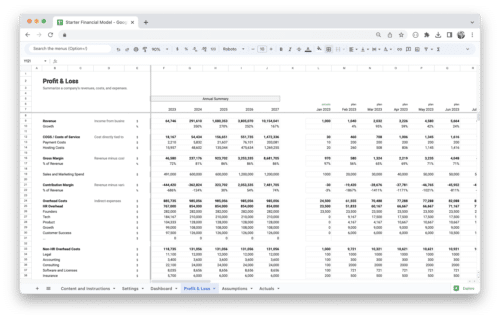
This is our Startup Profit and Loss Statement template. It is perfect for startups that want to get started with financial modeling. The template consists of the basics of our Standard Financial Model. Revenue and expense modeling can be easily added on top of this template, and you can adapt it for any type of business.
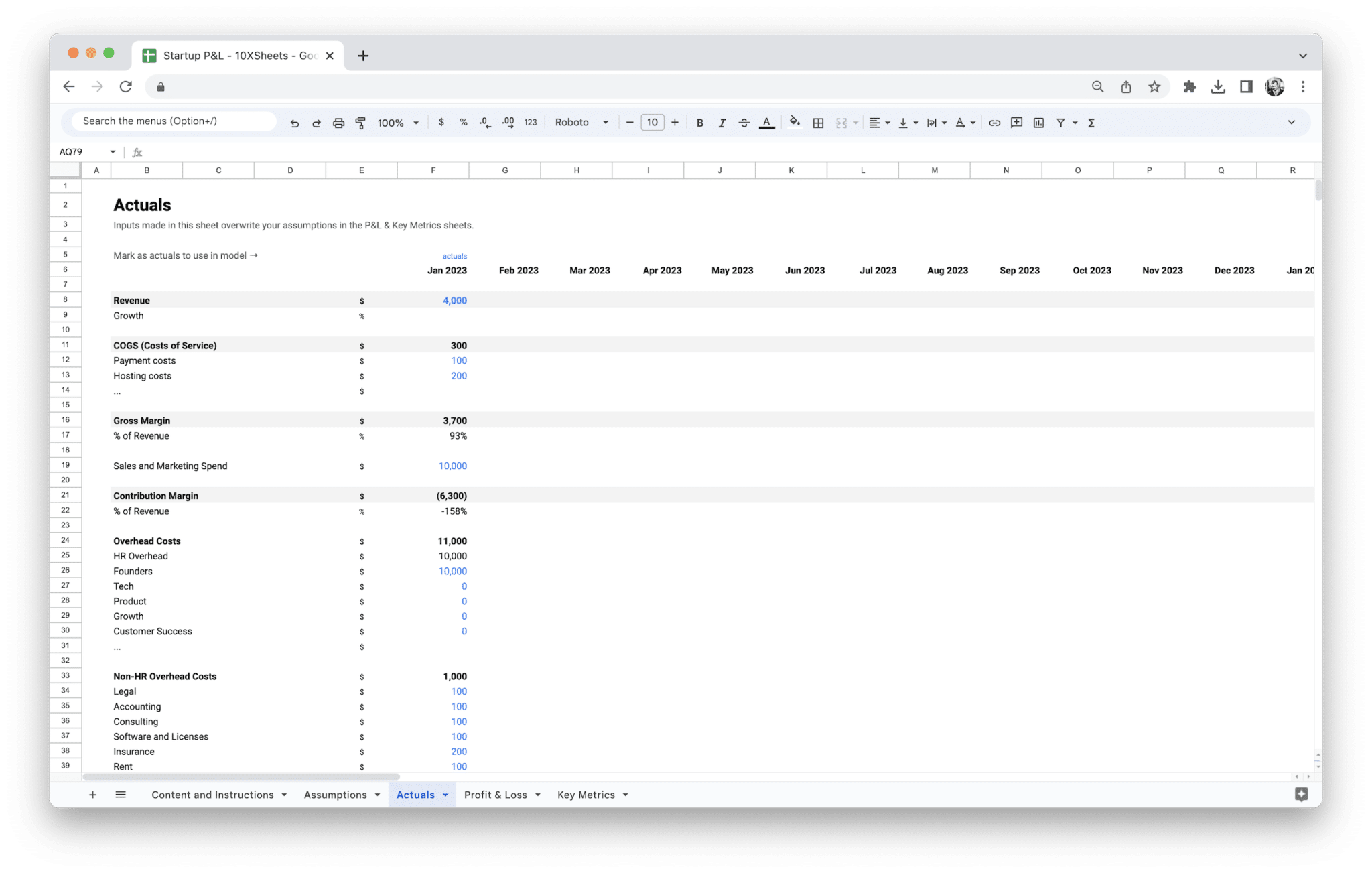
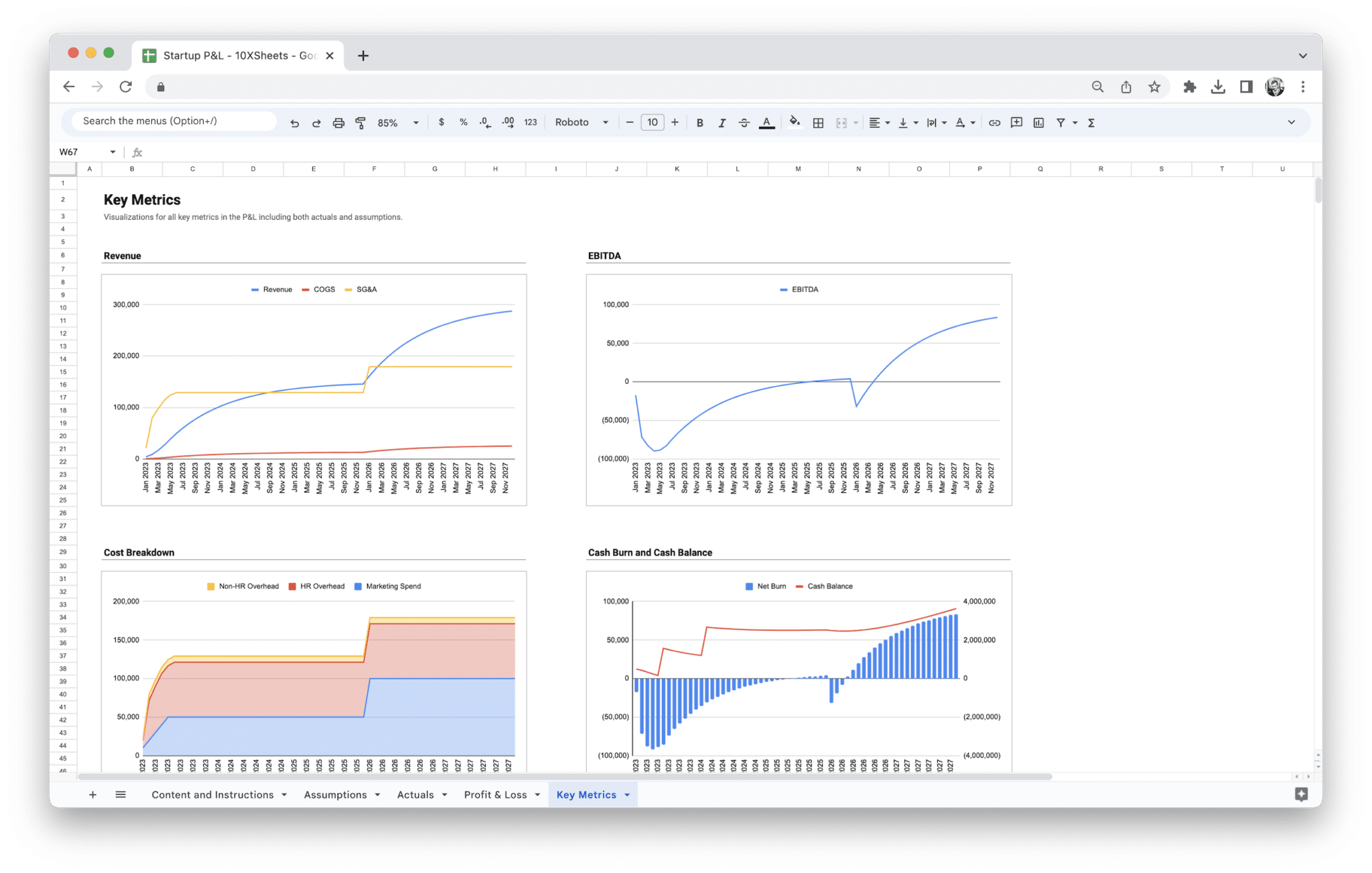
Apart from the Profit and Loss Statement, you’ll get separate actuals and assumptions sheets and a dashboard that visualizes key financial metrics.
We offer different P&Ls for different types of businesses as well as many other expert-built templates to get started with financial modeling.
Beyond templates, 10XSheets provides financial modeling-as-a-service to startups and small businesses. We create and maintain custom spreadsheet models for you. If you need assistance with implementation, customization, or maintenance do not hesitate to reach out.
Make a one-time payment and
enjoy your template forever.
No extra costs, no strings attached,
more savings for you.
Keep your templates up-to-date
with free access to regular updates.
Related products
-
Sale!
Startup Financial Model Template
$119.00Original price was: $119.00.$79.00Current price is: $79.00. -
Sale!
E-Commerce Profit and Loss Statement
$119.00Original price was: $119.00.$79.00Current price is: $79.00.