Marketplace Profit and Loss Statement
$119.00 Original price was: $119.00.$79.00Current price is: $79.00.
34% Off
Take control of your marketplace business finances, forecast your revenues and expenses, and track your financial performance with ease. With a customizable dashboard and separate Assumptions and Actuals sheets, you can easily stay organized and make informed decisions.
Description
Managing the finances of a marketplace can quickly become overwhelming. With multiple revenue streams, diverse expenses, and ever-changing costs, it can be difficult to keep track of everything and ensure your business remains profitable. Without a clear view of your financial health, it’s easy to miss opportunities for growth or overlook areas where you could be saving money.
Our Marketplace P&L Statement Template is designed to solve these challenges. This easy-to-use template provides a clear structure to track your revenue, expenses, and net profit. It helps you break down all your income sources—whether it’s marketplace fees, direct sales, subscriptions, or advertising—while categorizing all your expenses, from shipping and inventory to platform fees and marketing costs. By using this template, you can quickly assess your marketplace’s financial performance, identify profitable areas, and pinpoint where to cut unnecessary costs. With accurate, up-to-date financial records at your fingertips, you’ll be able to make smarter, data-driven decisions that support your marketplace’s growth and long-term success.
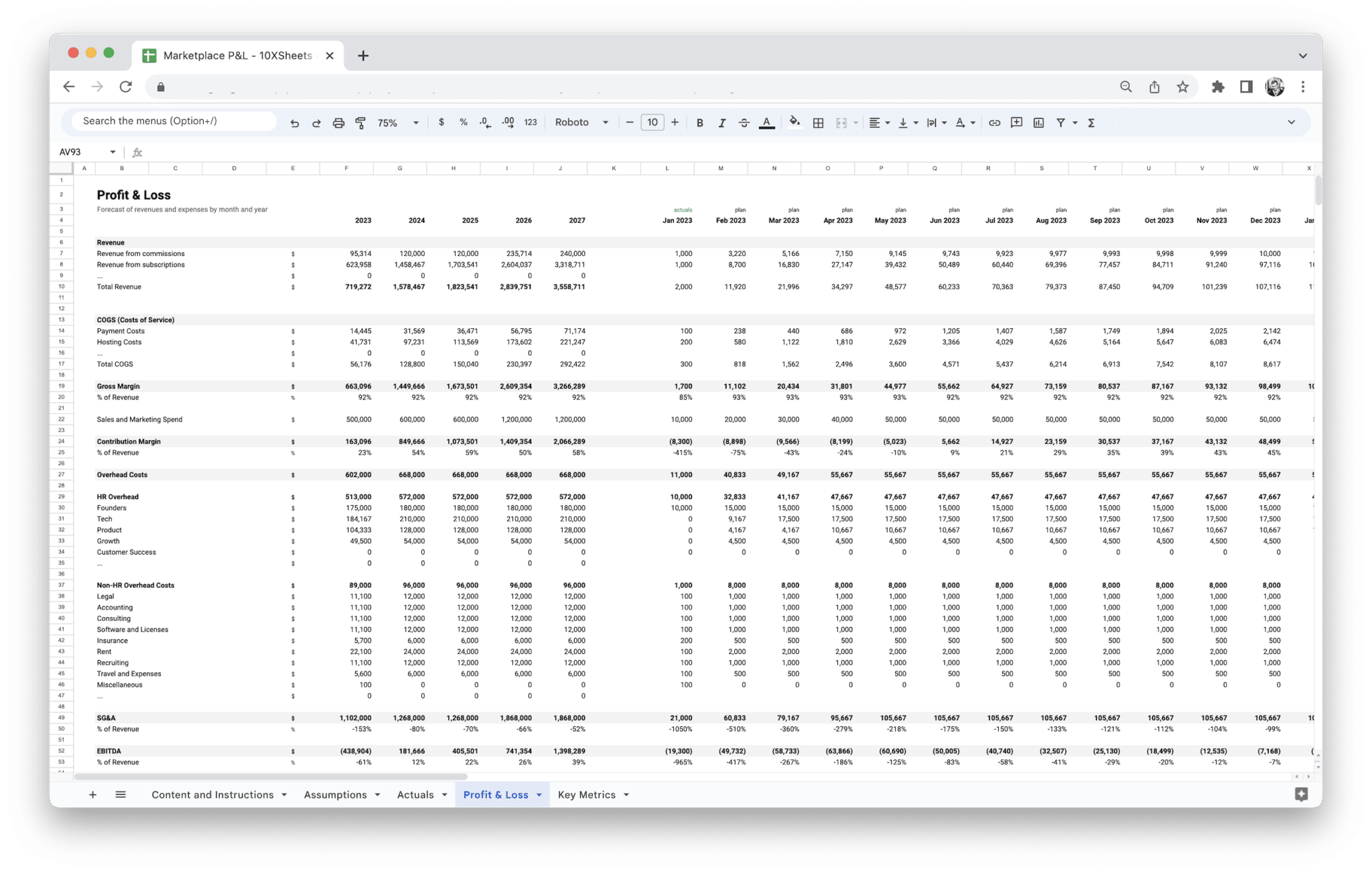
A Marketplace Profit and Loss (P&L) Statement is a financial report that summarizes the revenues, costs, and expenses incurred by an online marketplace over a specific period, such as a month, quarter, or year. It’s a snapshot of how well the business is performing financially, showing the balance between what is earned and what is spent. While the core idea behind a P&L statement remains the same across all types of businesses, its specific application in online marketplaces includes unique elements that reflect the digital and often multi-faceted nature of these businesses.
In the context of an online marketplace, the P&L statement provides a detailed view of all financial activities related to the platform’s operations. This includes revenue from various sources (such as marketplace fees, advertising income, and subscriptions) as well as the costs associated with running the platform, managing transactions, and fulfilling orders. Unlike traditional businesses that may have a simpler financial structure, marketplaces often deal with numerous revenue streams, third-party sellers, and complex operational costs, making a P&L statement an invaluable tool for understanding profitability.
The Importance of a Profit and Loss (P&L) Statement for Marketplace Businesses
Having a P&L statement is crucial for marketplace businesses because it gives clear insight into financial health and guides decision-making. Here are a few key reasons why it’s so important:
- Provides a clear overview of financial performance: The P&L statement helps you see whether your marketplace is profitable or if there are areas that need improvement.
- Helps track revenue and expenses: It allows you to monitor multiple revenue streams (e.g., marketplace fees, subscriptions, advertising) and track how much is spent in various areas like marketing, shipping, or platform fees.
- Supports strategic decision-making: By understanding the areas where money is coming in and going out, you can make more informed decisions about budgeting, scaling, or investing in new features.
- Aids in tax reporting and compliance: A P&L statement is essential for ensuring that all expenses and revenues are recorded correctly, which makes tax filing and compliance easier and more accurate.
- Improves financial forecasting: By analyzing past performance, you can project future revenue, expenses, and profitability, helping you plan for upcoming periods with more certainty.
- Builds trust with investors or stakeholders: If you’re seeking funding or investors, a well-maintained P&L statement provides transparency and demonstrates that you understand your business’s financial dynamics.
Key Benefits of Using a Template for Tracking Financial Performance
Using a template to track your marketplace’s profit and loss offers numerous advantages. Here are some key benefits:
- Saves time and reduces errors: A pre-designed template helps ensure that all necessary components are included, and formulas are set up for calculations, reducing the chance of manual errors.
- Simplifies financial tracking: Templates help organize financial data in a consistent and structured way, making it easier to understand and analyze.
- Helps monitor multiple revenue streams: With a template, you can track various income sources (such as marketplace fees, advertising, and subscriptions) in one place, allowing for a comprehensive view of your earnings.
- Provides clarity on profitability: By including detailed sections for both income and expenses, templates help you quickly identify whether your marketplace is profitable and pinpoint areas that may need attention.
- Enhances accuracy and consistency: Using a template ensures that the same categories and formats are followed each time, making your financial reports more consistent and reliable over time.
- Supports scalability: As your marketplace grows and diversifies, a template can easily be adjusted to accommodate new revenue streams and cost categories, ensuring that your financial tracking evolves with your business.
Key Components of a Marketplace P&L Statement
A Marketplace Profit and Loss Statement typically includes several important components that provide a clear breakdown of your financial performance. These components include:
- Revenue: The total income your marketplace earns, broken down by different streams such as marketplace fees, direct sales, subscription income, and advertising revenue.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): The direct costs associated with providing goods or services, including manufacturing costs, inventory management, and shipping.
- Operating Expenses: All other expenses necessary to run your marketplace, including marketing, platform fees, employee wages, and technology costs.
- Taxes and Deductions: Any applicable taxes or fees that need to be deducted from your revenue, such as sales tax, income tax, or platform commissions.
- Net Profit: The final amount left over after subtracting all costs, expenses, and taxes from your revenue. This is the key indicator of whether your marketplace is making money or incurring a loss.
Each of these components plays a vital role in understanding where your marketplace’s money is coming from and where it’s going. Accurately tracking and categorizing these components helps ensure your P&L statement is both comprehensive and useful.
How It Differs from Traditional Business P&L Statements
While the basic structure of a Profit and Loss statement remains the same across all types of businesses, a Marketplace P&L has several unique characteristics that distinguish it from traditional P&L statements used by non-marketplace businesses.
- Multiple revenue streams: Unlike traditional businesses, where revenue may come from one or two sources, a marketplace has multiple ways of earning money. These can include commission fees from sellers, subscription income, listing fees, advertising revenue, and other service-related income. A marketplace P&L needs to track these separately for a more granular view of profitability.
- Costs related to third-party sellers: Marketplaces are usually platforms that facilitate transactions between buyers and third-party sellers. This means that much of the cost structure involves transactions that are outside the marketplace’s direct control. These costs could include seller commissions, vendor payments, or platform fees, which are often shared between the platform and the sellers. Unlike traditional businesses, marketplaces need to account for these shared costs accurately.
- Complex expense structure: Traditional businesses typically deal with direct costs and general operational expenses. However, in a marketplace model, expenses can be more complex and include things like seller support, platform maintenance, and technology costs. A marketplace P&L needs to factor in the costs of maintaining and growing the platform itself, in addition to covering the usual expenses like payroll and marketing.
- Scalability and modularity: Unlike a traditional business that might have a fixed set of products or services, a marketplace can scale rapidly by adding new product categories, third-party sellers, or even expanding to new geographical areas. This growth often comes with new revenue streams and additional costs, which means the P&L statement must be flexible enough to incorporate these changes over time.
- Revenue sharing: Many marketplaces share a portion of the revenue with their sellers, especially in commission-based models. This adds an extra layer of complexity when calculating profits, as a portion of the earnings must be allocated to sellers and platform fees.
In essence, while both traditional businesses and marketplaces use P&L statements to assess their financial performance, the nature of a marketplace’s multi-faceted income and cost structure requires a more nuanced and flexible approach to financial tracking.
A Marketplace Profit and Loss Statement Template is an incredibly powerful tool for any marketplace business owner. It simplifies the often complex process of tracking your financial health and provides clear insights that can help you make smarter decisions. Here are the key benefits of using a template:
- Simplifies Financial Tracking: A template takes the guesswork out of financial reporting by providing a clear structure for recording revenue, expenses, and profits. This can save time and reduce the risk of errors compared to creating a P&L statement from scratch each time.
- Improves Accuracy: With pre-set formulas and fields for each type of income and expense, a P&L template minimizes the risk of misclassification and ensures consistency across your financial reports.
- Easier Financial Analysis: By breaking down your marketplace’s performance in a structured way, you can easily spot trends, pinpoint areas for improvement, and identify profitable revenue streams.
- Helps with Forecasting: Having a clear view of your marketplace’s financial data helps you predict future earnings, expenses, and growth. This can be crucial when planning for the next quarter or year.
- Enhances Decision Making: A P&L statement provides the hard data needed to make strategic business decisions, whether you’re looking to increase your marketing budget, adjust pricing, or evaluate the profitability of new revenue streams.
- Supports Tax Filing: The template can help you track the income and expenses you need for tax filings. By keeping your P&L up-to-date, you’ll ensure that you’re prepared when tax season rolls around and reduce the risk of costly mistakes.
- Facilitates Funding or Investment: When seeking funding or investors, a well-maintained P&L statement can help build credibility and demonstrate the financial health of your marketplace. Lenders and investors often ask to see a P&L as part of their decision-making process.
- Promotes Financial Transparency: A clear and accurate P&L statement helps ensure transparency in your financial dealings, whether you’re sharing it with stakeholders, partners, or employees. It promotes accountability and fosters trust.
- Tracks Profitability Over Time: By using a template consistently, you can track your marketplace’s profitability over time. This allows you to gauge whether you’re improving or losing ground in key areas such as revenue generation and cost management.
A Marketplace Profit and Loss (P&L) Statement is a comprehensive snapshot of your business’s financial performance over a specific period. It outlines your revenue streams, expenses, and net profit, helping you evaluate the health of your marketplace. Each component of the P&L provides insight into different aspects of your operations, and understanding these elements is essential for accurate financial tracking.
Revenue Streams
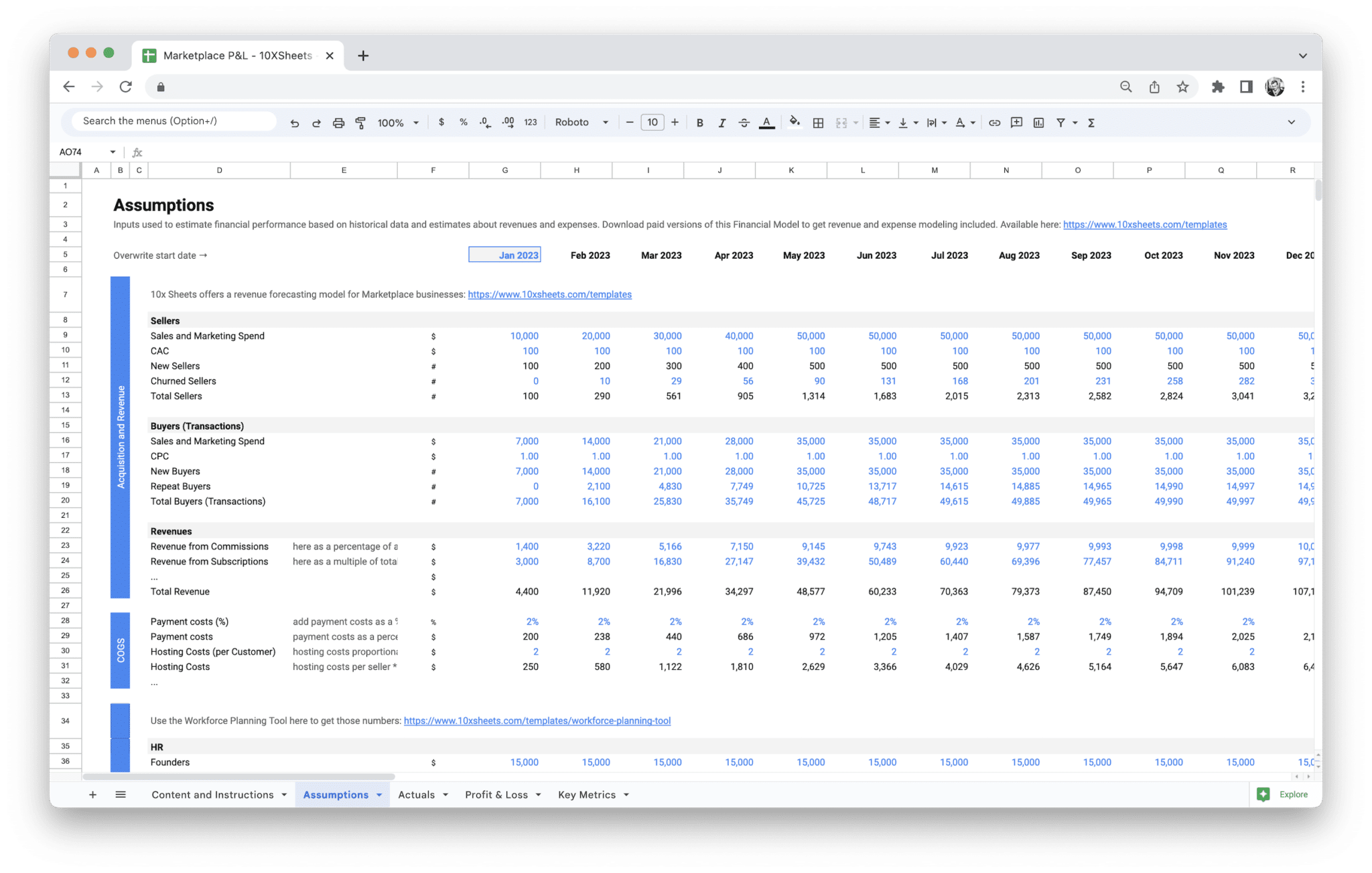
Revenue is the lifeblood of any marketplace, and breaking it down into distinct categories helps you gain a clear picture of where your money is coming from. For an online marketplace, revenue streams may include a combination of the following:
- Marketplace Fees: Most marketplaces charge a fee or commission on each transaction made on the platform. This could be a percentage of the sale price or a flat fee. The marketplace fee can vary depending on the type of goods or services being sold and the seller’s agreement with the platform. For instance, a marketplace might charge a 15% commission on a product sale but offer a discounted fee for subscription-based services.
- Direct Sales: If your marketplace sells products or services directly to customers, this becomes an important revenue stream. Direct sales are typically easier to track since you control the pricing and inventory. Depending on the nature of your business, direct sales might also include bundled offers, exclusive products, or services provided through the marketplace.
- Subscription Services: Some marketplaces generate recurring income through subscriptions. For example, sellers may pay monthly or annual fees for premium listing services, marketing, or access to exclusive features. Subscriptions can provide a steady, predictable stream of income and are often much more valuable for long-term planning than one-time product sales.
- Advertising and Sponsorship Income: Many online marketplaces monetize their platform further through advertising. Sellers or third parties may pay to advertise their products or services, either through sponsored listings, banner ads, or other marketing options. This form of revenue is increasingly popular, especially as marketplaces scale and attract more traffic.
Tracking each revenue stream individually allows you to understand what drives your income the most and optimize your platform accordingly. Are certain seller fees bringing in more money than others? Is your subscription model profitable enough to justify its costs? The answers to these questions help you focus your business efforts.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
The Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) refers to the direct costs associated with producing or acquiring the goods or services that your marketplace sells. These costs directly impact your gross profit, so accurately calculating COGS is crucial for assessing your marketplace’s profitability.
For a marketplace that sells physical products, COGS includes:
- Product Manufacturing or Purchase Costs: If you sell products directly, you’ll need to factor in the cost of manufacturing them or purchasing them from suppliers. For example, if you sell clothing, this would include the cost of raw materials, production labor, and factory overhead.
- Inventory Management Costs: Managing inventory incurs various costs, such as storage, warehousing, and inventory software. The longer products sit in storage, the more expensive they become due to both storage fees and the opportunity cost of not selling them.
- Shipping Costs: Shipping is another essential part of COGS. Whether you’re handling it yourself or passing the cost onto the customer, shipping fees for sending goods from your warehouse or suppliers directly to customers must be accounted for. This may include packaging, postage, and any fulfillment service charges.
If your marketplace acts as an intermediary between buyers and sellers (like eBay or Etsy), COGS may look a bit different. In this case, your COGS might focus more on transaction fees, payment gateway charges, and fraud prevention—expenses that are incurred as a result of facilitating sales, rather than producing or handling physical products.
Managing your COGS effectively ensures that your gross margin remains healthy. If your COGS are too high, it could reduce your overall profitability, even if your revenue is growing. Optimizing inventory turnover, finding cost-effective suppliers, and negotiating better shipping rates are all key ways to improve your COGS.
Operating Expenses
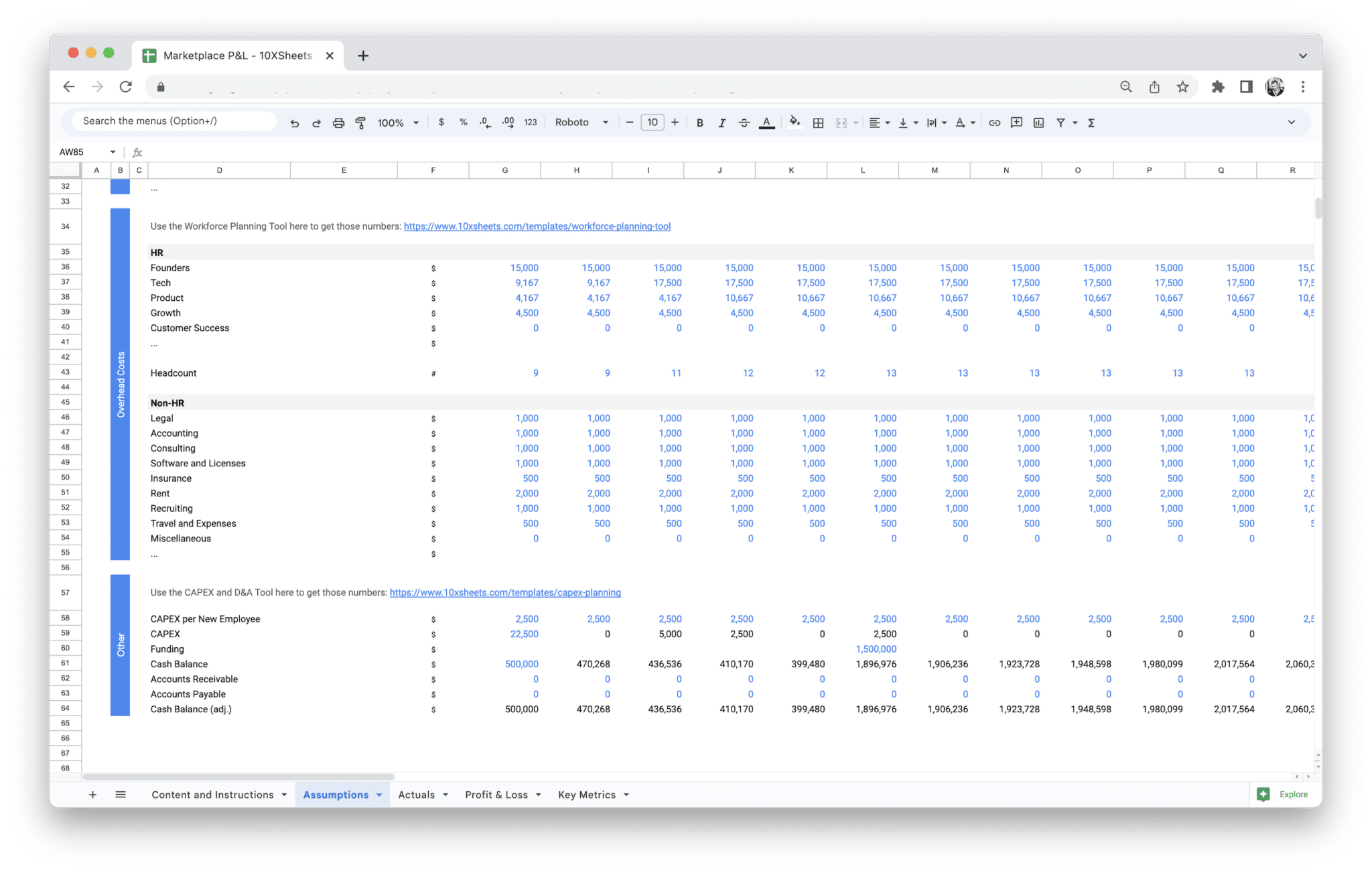
Operating expenses are the costs involved in running your marketplace on a day-to-day basis. Unlike COGS, which are directly tied to the production of goods or services, operating expenses are broader and include everything that keeps your business functioning smoothly.
Some of the most common operating expenses for a marketplace include:
- Platform and Hosting Fees: These are the costs of running your marketplace’s website or mobile app. This might include payments for web hosting, cloud storage, content management systems (CMS), and any related services.
- Marketing and Advertising Costs: Attracting new users and sellers to your platform requires a solid marketing budget. This can include both online and offline marketing efforts, such as paid search ads, social media marketing, influencer collaborations, and email campaigns.
- Employee Salaries and Benefits: If you have staff to manage the platform, customer service, technical support, or marketing, their salaries are a significant operating expense. This also includes benefits like health insurance, retirement contributions, and other perks.
- Software and Technology Costs: Marketplaces rely on various software tools to help with things like customer relationship management (CRM), accounting, email marketing, inventory tracking, and more. These software subscriptions can add up, especially if you’re using premium versions or integrating several different systems.
- Office Expenses: If your team works in a physical office, this category includes rent, utilities, office supplies, and equipment. Even if your business operates remotely, it might still incur some office-related costs, such as co-working space memberships or digital infrastructure expenses.
Operating expenses are critical to track, as they affect your overall profitability. A large portion of your operating expenses might be non-negotiable (like software subscriptions or employee salaries), but there are often opportunities to reduce costs in areas like marketing spend or office overhead.
Taxes and Other Deductions
Taxes can significantly impact your marketplace’s profitability, so it’s essential to include them in your P&L statement. These taxes can vary greatly depending on your location, your customer base, and the types of services or products you offer.
Some common taxes and deductions for online marketplaces include:
- Sales Tax: In many regions, you are required to collect sales tax on the items you sell. The rate can differ depending on where your customers are located and the tax laws in that region. For marketplaces with international customers, this can get complicated, as you may need to manage taxes in multiple jurisdictions.
- Income Tax: The money your marketplace earns is subject to income tax. The amount you owe will depend on your taxable income, which is calculated as your revenue minus your expenses. As a business owner, you’ll need to pay attention to your income tax obligations to avoid penalties and interest.
- Marketplace Commissions or Fees: In some cases, platforms like Amazon, eBay, or Etsy may charge sellers a commission on sales, and you may have to pass those costs on to your customers. These fees should be included in your expenses, as they reduce your profitability.
The more diligent you are in calculating taxes and other deductions, the more prepared you’ll be when it comes time to file. Keeping accurate records of tax payments and commissions ensures compliance with local laws and prevents any surprises at tax time.
Net Profit
Net profit is the most important number on your P&L statement. This is the money your marketplace earns after subtracting all costs, taxes, and other expenses from your revenue. It’s the bottom line that reflects the true profitability of your business.
To calculate net profit, you start with your total revenue and subtract all the direct and indirect costs involved in running your marketplace. These include:
- Revenue from Sales
- COGS
- Operating Expenses
- Taxes and Other Deductions
Once you’ve accounted for all these costs, what remains is your net profit. If the result is positive, it means you’ve earned a profit. If it’s negative, your marketplace has incurred a loss during that period.
Net profit is crucial because it directly informs your decision-making. Positive net profit means that your marketplace is healthy and can reinvest in growth initiatives, like expanding marketing campaigns or hiring more staff. Negative net profit signals that it’s time to revisit your cost structure or find ways to increase revenue. A consistent understanding of your net profit helps you maintain a sustainable and successful business.
By thoroughly analyzing all these components—revenue streams, COGS, operating expenses, taxes, and net profit—you can ensure that your Marketplace Profit and Loss Statement reflects the true financial health of your business. With this data, you’ll be better equipped to make informed decisions and optimize your marketplace for growth and profitability.
Creating a Marketplace Profit and Loss (P&L) Statement might seem intimidating at first, but once you break it down into steps, it becomes an essential and manageable part of your business management routine. The P&L statement is designed to help you track how much money you are bringing in and how much you’re spending. It provides clarity on whether your marketplace is financially healthy, and it’s a valuable tool when making decisions about scaling or adjusting your business strategy.
The key to creating an accurate and useful P&L statement is consistency and precision. Let’s walk through the process of creating one from start to finish.
Filling Out the Template
- Gather Financial Data The first step in preparing a P&L statement is to gather all relevant financial data. This includes:
- Revenue Information: Collect data from all your revenue streams, such as marketplace fees, direct sales, subscription fees, and advertising income. This might require you to pull reports from your sales platform, payment processors, or CRM system.
- Expense Details: Gather data on your costs, including both COGS (Cost of Goods Sold) and operating expenses. This might include invoices, receipts, and records for inventory costs, shipping expenses, salaries, marketing spend, platform fees, and other overheads.
- Tax Information: Ensure you have the necessary data on sales tax, income tax, and any other relevant deductions or obligations.
- Choose Your Timeframe A P&L statement can cover various time periods, such as a week, month, quarter, or year. For most marketplace owners, monthly or quarterly statements are most useful as they offer a manageable timeframe for tracking performance. Choose the period that makes the most sense for your business, depending on how often you want to assess your financial standing.
- Enter Revenue Data Start by entering your revenue sources into the appropriate sections of the template. For instance:
- Marketplace Fees: If you charge a commission for each sale on your platform, include the total amount of marketplace fees collected from sellers or customers. Break this down by seller or product category if necessary.
- Direct Sales: Enter the total amount from products or services you sold directly, whether through your marketplace or via any other direct-sales model.
- Subscriptions: If you offer subscription-based services or memberships, include all income from those services.
- Advertising Revenue: If you earn income from ads or sponsored listings on your platform, record that as well.
Ensure each source of revenue is listed separately, as it will help you analyze trends over time and understand which areas of your marketplace generate the most income.
- Enter Costs of Goods Sold (COGS) The next step is to enter the direct costs associated with producing or procuring the goods or services sold on your marketplace. This includes:
- Manufacturing or Purchase Costs: If you sell physical products, input the total amount spent on manufacturing or purchasing products.
- Shipping and Fulfillment: Enter costs related to shipping, handling, and fulfilling orders, whether you handle it internally or use a third-party fulfillment service.
- Inventory Management Costs: Include expenses such as warehousing fees, inventory software costs, and any other expenses directly related to storing and managing inventory.
Be thorough with these entries, as accurate COGS calculations are crucial to determining your gross profit and overall profitability.
- Enter Operating Expenses Now, move on to your operating expenses, which cover the ongoing costs of running your marketplace. These might include:
- Marketing and Advertising: Enter all costs related to attracting customers and promoting your marketplace, such as social media ads, influencer marketing, SEO services, and content creation.
- Platform and Software Fees: Include fees for your marketplace platform (e.g., monthly subscriptions to website hosting, payment processors, or e-commerce platforms) and any third-party software tools used for managing customer relationships, accounting, or inventory.
- Salaries and Wages: Input all payroll expenses, including employee wages, benefits, and any outsourced services (like customer service or IT support).
- Operational Overhead: Don’t forget to include smaller expenses like office supplies, utilities, and other daily operating costs.
Be as detailed as possible here, as this will give you a clearer picture of your business’s ongoing financial obligations.
- Calculate Net Profit After inputting your revenues and expenses, use the formulas in your template to calculate the net profit (or loss). Subtract your total expenses (COGS and operating expenses) from your total revenue. The result will be your net profit for the period. If this number is positive, you’re profitable; if it’s negative, you’ve incurred a loss.Your net profit will serve as a key performance indicator (KPI) for your business, helping you make decisions about cost-cutting or increasing revenue.
- Review and Analyze Once your data is entered and your net profit is calculated, take the time to analyze the results. Is your marketplace performing well, or are there areas that need improvement? If your costs are too high, are there places where you can reduce spending? If your revenue is lower than expected, are there opportunities to increase sales or expand your market reach?This review is where you start to make data-driven decisions that will help you steer your marketplace toward greater profitability.
Real-World Examples and Scenarios for Accurate Data Entry
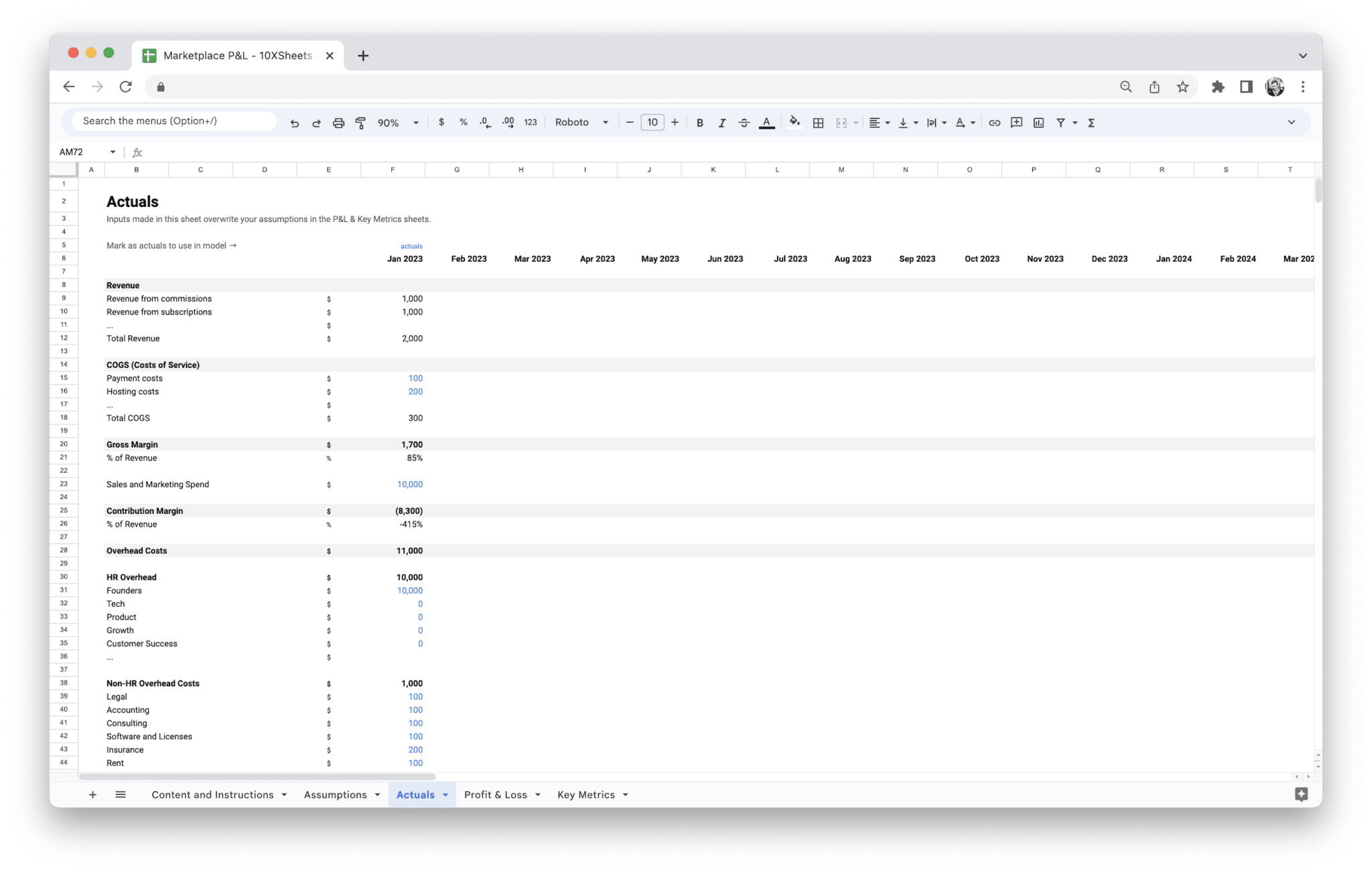
Let’s take a look at a real-world example to see how this process might work in practice. Suppose you run an online marketplace that sells custom-made furniture and charges a 10% commission on each sale. Your P&L statement might look like this:
- Revenue:
- Marketplace Fees: $10,000 (10% commission on sales)
- Direct Sales: $5,000 (sales of custom furniture)
- Advertising Income: $2,000 (from a vendor partnership)
- Cost of Goods Sold:
- Manufacturing Costs: $4,000 (raw materials and production labor)
- Shipping Costs: $500 (shipping furniture to customers)
- Inventory Management: $200 (warehouse fees)
- Operating Expenses:
- Marketing and Advertising: $1,000 (social media ads, influencers)
- Platform and Software Fees: $300 (website hosting, payment processor fees)
- Salaries: $2,500 (salary for a part-time employee managing customer service)
- Operational Overhead: $200 (utilities, office supplies)
After inputting these figures into your template, you would calculate your net profit as follows:
- Total Revenue: $10,000 + $5,000 + $2,000 = $17,000
- Total COGS: $4,000 + $500 + $200 = $4,700
- Total Operating Expenses: $1,000 + $300 + $2,500 + $200 = $4,000
- Net Profit: $17,000 (Revenue) – $4,700 (COGS) – $4,000 (Operating Expenses) = $8,300
So, in this case, your net profit is $8,300, which indicates that the marketplace is profitable. You can then analyze these numbers to decide if there are any areas to cut costs or improve revenue.
Tips on Keeping Records Up-to-Date and Maintaining Accuracy in Financial Reporting
Accurate financial reporting relies on keeping your records up-to-date and ensuring that data is entered consistently. Here are some practical tips for maintaining accuracy in your P&L statement:
- Use Accounting Software: If you haven’t already, consider using accounting software that integrates with your marketplace platform. This can automate data entry, reduce errors, and ensure real-time updates. Tools like QuickBooks, Xero, and FreshBooks offer P&L reporting features and can sync with payment processors and bank accounts.
- Regular Updates: Don’t wait until the end of the month or quarter to update your P&L statement. Try to update it weekly or biweekly to keep your records current. This will also help you catch any discrepancies or financial issues early on, rather than letting them accumulate.
- Organize Financial Documents: Keep your invoices, receipts, and bank statements organized. If you’re using digital tools, create separate folders for each type of expense or revenue, and store them in a way that’s easy to access. This will make data entry much faster and more efficient.
- Be Consistent with Categorization: When entering data into your P&L template, ensure you consistently categorize income and expenses in the same way each time. For instance, if you categorize marketing expenses under “Advertising” one month, do the same in subsequent months to maintain consistency.
- Reconcile Bank Accounts: Regularly reconcile your bank accounts to ensure that the numbers in your P&L statement match the actual transactions in your bank statements. This will help you avoid discrepancies that could lead to inaccurate reporting.
- Seek Professional Help When Needed: If your finances get complicated, or you’re unsure about how to classify certain transactions, don’t hesitate to consult a financial professional. An accountant or bookkeeper can help ensure that your P&L statement is accurate and that your business stays compliant with tax regulations.
By following these tips, you’ll not only maintain the accuracy of your financial reports but also gain a clearer understanding of your marketplace’s performance, enabling you to make better business decisions.
Your marketplace business is unique, and your P&L statement should reflect that. Customizing your template helps you capture the most relevant data and track the metrics that matter most to your business. Here’s how you can tailor a P&L statement template to fit your needs:
- Adjust for Business Size: Depending on whether you’re a small marketplace or a large enterprise, your P&L will look different. Make sure the template allows for multiple revenue streams and expense categories that fit your business model, such as adding categories for larger inventory or more extensive employee expenses.
- Add or Remove Categories: Customizing the template to include categories that apply specifically to your marketplace is key. For instance, if you offer subscription services, add a line item for “Subscription Revenue.” If you sell internationally, add columns to track currency exchange rates or regional sales taxes.
- Incorporate Industry-Specific Metrics: Your marketplace may have industry-specific metrics that should be tracked, such as customer acquisition costs, vendor payments, or royalty fees. Add these as line items in the expense or revenue sections to ensure you’re capturing all relevant data.
- Use More Granular Detail: If your marketplace has several types of products, services, or sellers, consider breaking down your revenue and costs into more specific categories. For example, instead of lumping all marketing expenses together, separate them into categories like “Digital Ads,” “Influencer Marketing,” and “Email Campaigns.”
- Tailor Tax Tracking: Different regions and jurisdictions have different tax laws, so make sure your template includes appropriate sections to track sales taxes, VAT, and any other regional taxes that apply to your marketplace.
- Integrate with Accounting Software: Many accounting platforms allow you to customize templates and integrate them with your existing software. This way, you can automatically pull in data from your marketplace platform, reducing manual data entry and improving accuracy.
- Personalize for Reporting: If you need to share your P&L with external stakeholders (e.g., investors, partners, or lenders), ensure that the template is designed for easy presentation. You may want to add graphs or visual summaries of your revenue and expense trends for quick analysis.
- Ensure Flexibility for Growth: As your marketplace evolves, you’ll likely need to add new categories or remove outdated ones. Choose a template that can adapt as your business grows, ensuring it remains relevant and useful at every stage of your company’s lifecycle.
While using a Marketplace Profit and Loss Statement Template is an excellent way to stay organized and track your financial health, there are several common mistakes that can lead to inaccurate results or missed opportunities. Here’s a list of mistakes to avoid:
- Neglecting Regular Updates: One of the most common mistakes is failing to update the P&L statement regularly. Inaccurate or outdated data can lead to poor decision-making and missed opportunities to adjust your business strategy.
- Misclassifying Expenses or Revenue: Be sure to accurately categorize all income and expenses. Misclassifying costs, such as grouping advertising spend with operating expenses, can distort your profit margins and affect the usefulness of the report.
- Ignoring Non-Financial Factors: Sometimes, a P&L statement focuses too much on hard financial numbers without considering external factors that can affect profitability, such as market trends, seasonality, or new product launches. Always keep broader business strategies in mind when reviewing your P&L.
- Overlooking Minor Expenses: Small costs can quickly add up over time. Don’t forget to include every expense, no matter how small, as they can have a significant impact on your overall profitability. For example, small subscription fees for tools or software might seem insignificant, but they accumulate.
- Not Considering Taxes Properly: Taxes are often one of the most overlooked areas in P&L statements. Failing to account for sales tax, VAT, or income tax can result in errors and lead to unexpected liabilities. Always ensure that your tax deductions and liabilities are correctly included in your expenses.
- Forgetting Depreciation: If your marketplace has significant assets (e.g., office equipment, vehicles, or computers), you need to account for depreciation in your P&L statement. Failing to do so can overstate your profits and mislead financial analysis.
- Not Keeping Accurate Receipts or Documentation: A P&L statement is only as accurate as the data you enter into it. If you don’t have proper documentation for your income and expenses, you risk entering incorrect figures. Keep receipts, invoices, and transaction records organized and accessible for easy entry into your template.
- Relying Too Much on Estimated Numbers: While estimates can be helpful in certain situations, relying too much on them in your P&L statement can lead to inaccuracies. Whenever possible, use actual figures from your financial records to ensure accuracy and reliability in your reporting.
- Failing to Customize the Template for Your Business: Using a generic P&L template without tailoring it to the specific needs of your marketplace can lead to missing key categories or misrepresenting your business’s financial performance. Make sure your template accurately reflects your unique revenue streams and costs.
- Not Reviewing the P&L Statement Regularly: A P&L statement should be a living document that you review regularly, not just at the end of the year. By checking your P&L periodically, you can catch any potential errors, stay on top of your finances, and make adjustments before small problems become big ones.
Avoiding these common mistakes will help you get the most out of your Marketplace Profit and Loss Statement Template, allowing you to make better financial decisions and keep your marketplace on track for success.
Get Started With the Marketplace P&L Statement!
This Marketplace P&L is designed to forecast revenues and expenses for Marketplace businesses.
The model contains:
- Content and instructions to get you started
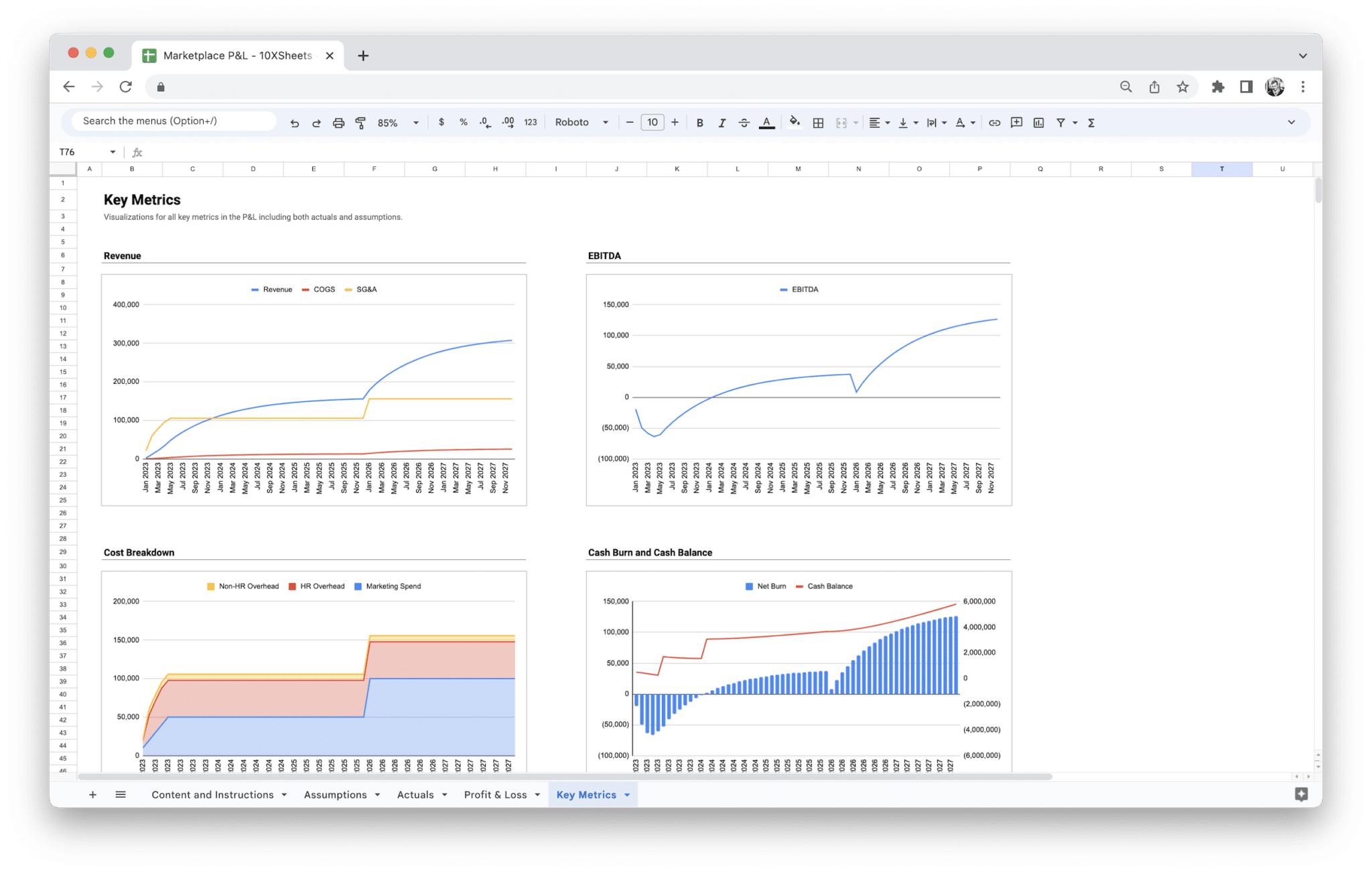
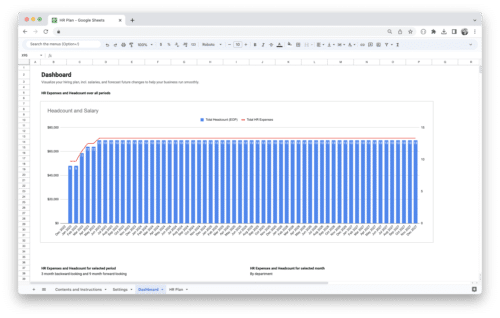
- A dashboard to visualize key financial metrics month by month
- P&L
- Separate Assumptions and Actuals sheets
If you need help implementing this model, 10X Sheets offers Financial Modeling as a Service. We can assist with all financial modeling matters.
Make a one-time payment and
enjoy your template forever.
No extra costs, no strings attached,
more savings for you.
Keep your templates up-to-date
with free access to regular updates.
Related products
-
Sale!
E-Commerce Financial Model Template
$219.00Original price was: $219.00.$149.00Current price is: $149.00.