Are you curious about which finance jobs offer the highest salaries? The finance industry is packed with opportunities to earn a substantial income, but with so many roles to choose from, it can be difficult to know where to focus. From managing investments and advising companies to assessing risk and ensuring financial stability, there are plenty of high-paying roles across various sectors.
Whether you’re interested in working for a major investment bank, a hedge fund, or helping individuals grow their wealth, the finance world has positions that offer lucrative salaries, attractive bonuses, and room for growth. In this guide, we’ll dive into the top-paying finance careers, what they involve, and how much you can expect to earn, so you can make an informed decision about where to take your career next.
Understanding Finance Jobs
The finance industry is vast and multifaceted, encompassing a wide range of roles and responsibilities that are critical to the functioning of both businesses and the global economy. From investment banking to corporate finance, risk management, and wealth management, finance professionals work in almost every industry, managing and optimizing the flow of money, capital, and assets. This industry plays a crucial role in driving economic growth by enabling companies to raise capital, invest in new projects, and manage financial risks. It also provides individuals and institutions with financial advice, investment opportunities, and strategies to manage their wealth.
Finance professionals typically work in banks, insurance companies, asset management firms, hedge funds, private equity firms, and corporations. They analyze financial data, create models, advise clients, and make strategic decisions that can have significant impacts on businesses and markets worldwide. The finance sector is also home to some of the most well-paid professionals, making it an attractive career choice for those with the right skills and qualifications.
Importance of High-Paying Jobs in Finance
High-paying jobs in finance not only offer significant earning potential but also provide an opportunity to work in dynamic and impactful sectors. For individuals seeking both financial rewards and career growth, these positions can lead to job satisfaction and long-term financial security. Here are some reasons why high-paying jobs in finance are so important:
- High earning potential: Finance offers some of the highest-paying roles across industries, with competitive salaries and performance-based bonuses that can result in six-figure or even seven-figure earnings.
- Career growth opportunities: Many high-paying finance jobs come with the chance to advance quickly, especially as you gain experience and build a network within the industry.
- Job stability: Finance professionals are in high demand, particularly those with specialized skills in areas like investment banking, wealth management, and quantitative finance. This demand leads to job security and stability in the long run.
- Impact on the economy: Finance professionals play a crucial role in shaping the economy by allocating capital, managing risk, and ensuring the financial health of organizations and governments.
- Global opportunities: Many finance jobs offer international opportunities, allowing professionals to work with global companies, clients, and markets.
Top High-Paying Finance Careers
The finance industry offers a variety of high-paying career paths that appeal to individuals with diverse skill sets. From managing investments to advising companies on financial strategies, these roles often come with significant responsibilities but also exceptional compensation. Whether you’re just starting in the finance field or looking to switch careers, knowing which positions offer the best salaries can help you set your sights on the most rewarding roles.
Finance jobs are known for offering competitive salaries, and many of these positions come with additional perks like performance bonuses, stock options, and the opportunity for advancement. As businesses and economies continue to grow, the need for skilled financial professionals is expected to rise, making finance a lucrative and stable career choice. Below are some of the top-paying roles within the finance sector, offering excellent opportunities for those looking to maximize their earning potential.
Investment Banking
Investment banking is one of the most prestigious and high-paying areas within finance. Investment bankers are responsible for helping companies and governments raise capital, as well as providing advisory services on mergers and acquisitions (M&A), restructurings, and other financial transactions. The long hours and high pressure often associated with investment banking are compensated with some of the highest salaries in finance.
Roles in investment banking include analysts, associates, vice presidents, and managing directors. Entry-level analysts can earn significant salaries, with bonuses often making up a large portion of their total compensation. As you climb the ranks to more senior roles like managing director, salaries can reach into the seven figures, especially with lucrative bonuses tied to deal-making success.
Private Equity and Venture Capital
Private equity (PE) and venture capital (VC) are investment firms that provide funding to businesses in exchange for equity ownership. PE firms typically invest in more mature companies, while VC firms focus on high-growth startups. Both sectors offer substantial financial rewards, with professionals working to maximize returns for their investors.
Private equity and venture capital professionals often start as analysts or associates and advance to senior roles such as principal or partner. These professionals are heavily involved in sourcing and evaluating investment opportunities, managing portfolios, and executing deals. As with investment banking, compensation in these fields can be highly performance-based, with top earners making millions, particularly in successful funds.
Hedge Fund Management
Hedge funds are investment vehicles that use a variety of strategies to generate returns for their investors, including long and short positions, leveraging, and derivatives. Hedge fund managers are responsible for developing and implementing these strategies, and their compensation is typically tied to the performance of the fund.
The most high-paying roles in hedge funds are those of portfolio managers and fund managers, who oversee the day-to-day operations of the fund and make key investment decisions. These professionals often earn base salaries in the six-figure range, but their total compensation can soar when the fund performs well, with bonuses and profit-sharing arrangements significantly boosting their earnings.
Corporate Finance
Corporate finance professionals are responsible for managing a company’s finances, including budgeting, forecasting, and financial planning. These professionals ensure that companies have the necessary capital to fund their operations, investments, and growth strategies. High-paying roles in corporate finance include financial analysts, controllers, treasurers, and chief financial officers (CFOs).
CFOs, the top financial executives in a company, typically earn substantial salaries, often exceeding $200,000 per year. Bonuses, stock options, and other incentives can further increase their total compensation. As CFOs play a critical role in shaping a company’s financial future, their compensation reflects the significant responsibility they hold.
Wealth Management and Financial Planning
Wealth management and financial planning are fields focused on helping individuals and families manage their financial assets. Professionals in this area advise clients on investments, estate planning, tax strategies, and retirement planning. High-net-worth individuals (HNWI) and ultra-high-net-worth individuals (UHNWI) typically rely on wealth managers for more comprehensive and tailored financial advice.
Wealth managers and financial planners often earn high salaries, particularly when working with high-net-worth clients. Compensation is often performance-based, with wealth managers earning a significant portion of their income through fees and commissions. Senior wealth managers can earn six or seven figures depending on the size of their client base and the complexity of the services they provide.
Risk Management and Compliance
Risk management and compliance professionals play an essential role in identifying, assessing, and mitigating financial risks within an organization. These roles are particularly crucial in financial institutions, such as banks and investment firms, where the stakes are high, and the potential for financial loss is significant.
High-paying roles in this field include risk managers, compliance officers, and chief risk officers (CROs). CROs, who oversee an organization’s entire risk management strategy, can earn substantial salaries, particularly at large financial institutions. These roles often come with additional performance-based bonuses tied to the organization’s ability to manage risks effectively.
Quantitative Finance
Quantitative finance is a field that combines finance, mathematics, and computer science to develop complex models and algorithms for trading, investing, and risk management. Professionals in this field, known as quants, use advanced statistical and computational techniques to analyze financial data and make predictions about market movements.
Quantitative analysts (quants) and financial engineers are in high demand, particularly in hedge funds, investment banks, and proprietary trading firms. These roles typically offer high salaries, with quants earning base salaries in the range of $100,000 to $200,000, with the potential for performance bonuses and profit-sharing arrangements. Senior quants and financial engineers at top firms can earn salaries in the millions, particularly when their models and strategies are successful.
Chief Investment Officer (CIO)
The Chief Investment Officer (CIO) is the top executive responsible for an organization’s investment strategy. In large financial institutions, pension funds, or insurance companies, the CIO oversees the management of investments and ensures that the company’s capital is deployed effectively to generate returns. They manage large portfolios, collaborate with analysts, and make key investment decisions.
CIOs typically earn substantial base salaries, with compensation packages that include performance-based bonuses and profit-sharing options. Due to the high level of responsibility, senior CIOs can command compensation well into the seven figures, particularly at major institutions.
Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) Advisor
Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) advisors specialize in guiding companies through complex transactions such as mergers, acquisitions, and divestitures. They conduct detailed financial analyses, negotiate deal terms, and advise clients on the strategic and financial implications of each deal. These professionals are crucial in high-stakes corporate restructuring, where their expertise can make or break the success of a deal.
M&A advisors are typically compensated with large base salaries and generous bonuses tied to deal success. Senior advisors or partners in top firms can earn millions, especially in high-profile transactions.
Asset Manager
Asset managers are responsible for managing investment portfolios on behalf of institutional clients, high-net-worth individuals, or mutual funds. They make decisions about buying, selling, and holding assets to achieve financial goals, including capital appreciation and income generation. Asset management professionals need to have a strong grasp of global markets, as they deal with stocks, bonds, real estate, and other investment vehicles.
Senior asset managers or portfolio managers at major firms can earn base salaries of $150,000 to $300,000, with bonuses and profit-sharing arrangements potentially pushing their total compensation into the millions.
Financial Risk Analyst
Financial risk analysts assess the risks associated with various investment opportunities and financial decisions. They analyze market trends, credit risks, liquidity risks, and operational risks to identify potential threats to an organization’s financial stability. Financial risk analysts are essential in ensuring that companies or financial institutions do not make risky decisions that could lead to significant financial losses.
With a keen eye for detail and strong analytical skills, financial risk analysts can earn competitive salaries, particularly in senior positions like senior risk analyst or risk manager, where salaries range from $100,000 to $200,000, with substantial bonuses based on performance.
Tax Director
Tax directors oversee all aspects of a company’s tax strategy and planning. They ensure that a company’s operations and financial practices comply with tax laws, help minimize tax liabilities, and ensure that financial records reflect proper tax treatment. Tax directors play an essential role in advising on mergers, acquisitions, and international tax regulations, ensuring that the company’s tax exposure is well-managed.
This highly specialized role commands high compensation, particularly in large corporations and global firms. Tax directors typically earn between $150,000 and $300,000 annually, with the potential for significant bonuses based on the company’s tax performance.
Real Estate Investment Manager
Real estate investment managers are responsible for overseeing real estate portfolios, which may include commercial, residential, and industrial properties. These professionals analyze market conditions, acquire properties, and manage investment strategies to maximize returns for their investors. They work in firms that specialize in real estate funds or within the real estate departments of large investment firms.
Senior real estate investment managers can earn significant salaries, often in the range of $150,000 to $300,000 annually, with bonuses and profit-sharing opportunities pushing their total compensation into the seven-figure range.
Financial Controller
The role of a financial controller involves overseeing the preparation of financial reports, managing internal controls, and ensuring the accuracy of financial records within an organization. Controllers are responsible for ensuring that financial reporting meets regulatory requirements and that financial statements are compliant with accounting standards.
Senior financial controllers or accounting directors can expect to earn a salary in the range of $120,000 to $200,000 annually, with bonuses and additional incentives pushing their total earnings even higher.
Equity Analyst
Equity analysts specialize in researching and evaluating stocks, providing investment recommendations based on their analyses of company performance, financial health, and market conditions. They often work for investment banks, asset management firms, and hedge funds, where their insights help drive portfolio decisions.
Equity analysts in top firms can earn salaries ranging from $90,000 to $150,000, with the potential for additional bonuses based on the performance of their recommendations. Experienced equity analysts at senior levels can easily earn over $300,000 per year, particularly in specialized areas like technology or healthcare.
Credit Analyst
Credit analysts evaluate the creditworthiness of individuals, companies, and governments by analyzing financial statements, economic trends, and credit data. Their role is to assess whether borrowers are likely to repay loans and meet their financial obligations. Credit analysts are especially important in banking, bond ratings, and lending institutions.
Credit analysts in senior roles, such as senior credit analysts or credit managers, can expect to earn between $100,000 and $150,000 annually, with significant bonuses for those working in high-volume, high-risk sectors like corporate lending and debt structuring.
Chief Executive Officer (CEO) in Finance
While not unique to the finance sector, the role of CEO in a financial organization such as an investment firm, bank, or insurance company is one of the most lucrative positions in the industry. The CEO is responsible for the overall strategy, operations, and success of the organization, guiding the company through complex financial landscapes and ensuring profitability and growth.
CEOs in the finance industry can earn base salaries ranging from $300,000 to $500,000, but their total compensation often includes equity grants, performance bonuses, and stock options, which can push their earnings into the tens of millions, especially in large publicly traded firms.
The finance industry offers a diverse array of high-paying careers, each with unique opportunities and challenges. Whether you’re interested in investment banking, hedge fund management, corporate finance, or wealth management, these roles provide significant earning potential and career growth. However, the path to success in finance often requires a combination of advanced education, specialized skills, and a strong work ethic. If you’re aiming for a top-paying job in finance, understanding the demands and rewards of each role will help you make an informed decision and plan your career path accordingly.
Investment Banking
Investment banking plays a pivotal role in the global finance industry, serving as a bridge between large corporations, governments, and investors. The primary function of investment banks is to help these entities raise capital, whether through issuing stocks, bonds, or facilitating mergers and acquisitions. Investment banks also provide advisory services, helping businesses navigate complex financial challenges, and structure deals that enable growth and expansion.
Investment bankers often work long hours, navigating high-pressure environments. However, the financial rewards are significant, with lucrative base salaries and substantial bonuses for those who excel in the industry.
High-Paying Positions Within Investment Banking
Investment banking offers a range of high-paying positions that escalate in terms of responsibility and compensation as you climb the corporate ladder. Some of the most sought-after roles include:
- Investment Banking Analyst: This is usually the entry-level position within investment banking. Analysts are tasked with conducting research, building financial models, and helping manage the day-to-day operations of deals. While the hours can be demanding, the compensation for analysts is generally competitive, particularly when factoring in bonuses.
- Investment Banking Associate: After a few years of experience or an MBA, you can move into an associate role. Associates manage the junior team, play a more direct role in client interaction, and often oversee the structuring of financial models and presentations. Their compensation increases significantly, with larger bonuses based on the deals they help close.
- Vice President: Vice presidents handle the relationships between clients and the bank. They take a leadership role in executing deals, managing analysts and associates, and overseeing the overall strategy. The position offers high pay, especially with performance bonuses.
- Managing Director: At the top of the pyramid are the managing directors. These professionals generate business for the firm, maintain key client relationships, and oversee significant deals. As the highest-ranking individuals in investment banking, managing directors can earn millions annually, particularly if their deals are successful.
Required Skills and Qualifications
To succeed in investment banking, a mix of technical and interpersonal skills is essential. Key qualifications include:
- Strong Analytical Abilities: Investment banking involves heavy financial analysis. Being able to read and understand financial statements, build complex models, and forecast future trends is crucial.
- Attention to Detail: The success of deals often depends on small details that may make or break a transaction. Accuracy and precision in financial modeling and reporting are vital.
- Communication Skills: Since investment bankers regularly work with clients and collaborate with other departments, clear and concise communication skills are necessary. This includes writing reports, presenting proposals, and negotiating deal terms.
- Work Ethic: Investment banking is known for its intense work culture. The ability to work long hours and under pressure is a must.
- Educational Background: Most investment bankers have a degree in finance, economics, or a related field. Many also have MBAs from top business schools, which significantly enhance career prospects.
Typical Salary Ranges and Potential Bonuses
Investment banking offers some of the highest salaries in finance, especially when factoring in performance-based bonuses. A typical salary breakdown for investment bankers can look like this:
- Analyst: The base salary typically ranges between $85,000 and $100,000 annually, but with bonuses, total compensation can rise significantly, often reaching $150,000 to $200,000 per year.
- Associate: Associates can earn between $150,000 and $200,000 in base salary, with bonuses that can push their total compensation to $300,000 or more annually.
- Vice President: Vice presidents in investment banking can make anywhere from $200,000 to $300,000 in base salary. With performance bonuses, total compensation can range from $500,000 to $700,000 or more.
- Managing Director: Managing directors typically earn base salaries of $400,000 to $500,000, but with bonuses, commissions, and profit sharing, their total earnings can exceed $1 million per year.
Private Equity and Venture Capital
Private equity (PE) and venture capital (VC) are two distinct but closely related sectors within finance that focus on investing in businesses with the aim of achieving high returns. While private equity tends to focus on acquiring and improving established companies, venture capital is more about investing in early-stage startups with high growth potential. Both sectors are highly competitive, and the stakes—and rewards—are incredibly high.
The primary function of PE and VC professionals is to identify lucrative investment opportunities, manage portfolios, and deliver significant returns for their investors. With their lucrative salary structures and substantial bonuses, professionals in these sectors can build significant wealth over time.
Key Job Titles in Private Equity and Venture Capital
Several key roles exist within private equity and venture capital, each offering the opportunity for substantial earnings. Some of the most prominent job titles include:
- Private Equity Analyst: Analysts typically perform research on potential investments, conduct financial modeling, and assist in due diligence processes. This is an entry-level position, but the compensation is generally high compared to other finance roles.
- Private Equity Associate: As associates, you’ll have more responsibility, including managing parts of transactions and client relationships. You’ll still conduct research and analysis but will also be expected to help manage portfolio companies and play a larger role in executing deals.
- Private Equity Vice President: Vice presidents oversee teams of analysts and associates, working closely with partners to drive the investment strategy and execute deals. As you gain experience, you’ll have more influence on which investments are pursued.
- Private Equity Partner: Partners are responsible for raising funds, generating deals, and managing relationships with investors. They have the final say on investments and are compensated based on the performance of the funds they manage. This is the most lucrative position in private equity.
- Venture Capital Analyst: Similar to analysts in PE, VC analysts focus on identifying potential startup investments and conducting due diligence. While VC is riskier than PE, it can also lead to incredibly high returns, especially in successful exits.
- Venture Capital Partner: Partners are the most senior professionals in VC, responsible for sourcing, investing, and exiting deals. Their compensation is often tied to the success of the funds they manage, with massive earnings potential.
Skills and Experience Needed for Success
To thrive in private equity or venture capital, you’ll need a specific set of skills and experiences:
- Financial Acumen: Strong skills in financial analysis, including financial modeling, valuation, and due diligence, are critical for assessing potential investments.
- Entrepreneurial Spirit: Particularly in venture capital, an ability to recognize high-growth opportunities and identify successful business models is key.
- Negotiation Skills: Whether you’re closing a deal in private equity or negotiating funding terms in venture capital, strong negotiation abilities are essential.
- Networking Abilities: Building relationships with entrepreneurs, business owners, and other investors is crucial to accessing the best deals and driving business growth.
- Educational Background: A background in finance, economics, or business is important. Many professionals in this field hold MBAs from top-tier business schools, which are often required for more senior positions.
Salary Expectations and Potential for High Earnings
Salaries in private equity and venture capital can vary widely depending on experience, firm size, and performance. Here’s a breakdown of salary ranges:
- Analyst: Analysts in both PE and VC typically earn between $100,000 and $150,000 in base salary. Bonuses and performance-based compensation can significantly boost this amount, pushing total compensation to $200,000 or more.
- Associate: Base salaries for associates range from $150,000 to $200,000, with total compensation reaching up to $400,000 depending on the firm’s performance.
- Vice President: VPs can expect to earn $200,000–$300,000 in base salary. With bonuses and a share of profits, they can earn upwards of $600,000 annually.
- Partner: Partners, as the most senior professionals, can earn base salaries between $500,000 and $1 million, with performance bonuses and equity stakes leading to earnings of $2 million or more in high-performing firms.
Hedge Fund Management
Hedge funds are pooled investment funds that use a wide range of strategies to generate high returns for their investors. These strategies often involve high levels of risk, including short selling, leverage, and the use of derivatives. Hedge fund managers are responsible for making investment decisions that align with their fund’s strategy, whether it’s long/short equity, macroeconomic bets, or global market strategies.
Hedge funds are often associated with high salaries, but the compensation structure can be complex, with fund managers earning a significant portion of the fund’s profits. As with private equity, the potential for high earnings exists, especially for top performers who successfully navigate the markets.
High-Paying Roles Within Hedge Funds
The hedge fund industry offers various high-paying roles. Here are some key positions:
- Hedge Fund Analyst: Analysts in hedge funds research markets, track economic trends, and assess financial data to identify opportunities for the fund to exploit. Entry-level analysts typically earn strong base salaries, with performance bonuses based on the fund’s returns.
- Hedge Fund Trader: Traders are responsible for executing the fund’s trades. They buy and sell securities based on the fund’s strategy, and their ability to act quickly and make profitable decisions is key to their success.
- Hedge Fund Portfolio Manager: Portfolio managers oversee the entire portfolio of the hedge fund, making key investment decisions and managing risk. This is a senior role with significant earning potential, particularly when it comes to bonuses linked to the performance of the fund.
- Hedge Fund Principal: Principals are senior-level managers who are directly involved in fund operations, fundraising, and managing investor relations. They have substantial equity stakes in the fund and earn a portion of the profits generated by the fund’s investments.
Required Qualifications and Expertise
To succeed in hedge fund management, you’ll need a solid foundation in finance, advanced knowledge of trading strategies, and a deep understanding of global financial markets. Key qualifications include:
- Strong Analytical Skills: You’ll need to be able to analyze complex data, forecast market trends, and make data-driven decisions quickly.
- Risk Management Expertise: Since hedge funds often deal with high-risk investments, understanding how to manage and mitigate risk is a must.
- Advanced Education: Most hedge fund managers hold advanced degrees, such as MBAs or specialized degrees in finance or economics. Many also hold certifications like the CFA (Chartered Financial Analyst).
Salary Potential and Bonus Structures
Salaries in hedge funds are typically high, but the compensation structure is heavily reliant on performance. Here’s a breakdown:
- Analyst: Hedge fund analysts generally earn between $100,000 and $150,000 in base salary, but performance bonuses can significantly increase this amount, often bringing total compensation to $200,000–$300,000 annually.
- Trader: Traders can earn base salaries of $150,000–$200,000, with total compensation often exceeding $500,000 when factoring in performance bonuses.
- Portfolio Manager: Portfolio managers can earn base salaries of $250,000–$400,000. With performance bonuses tied to the fund’s success, they can earn millions, especially if the fund delivers exceptional returns.
- Principal: Principals often earn base salaries of $500,000 or more, but the bulk of their earnings comes from performance-based compensation, which can lead to earnings of several million dollars annually.
Corporate Finance
Corporate finance plays a central role in how businesses manage their financial resources, making decisions that directly impact the company’s long-term profitability and financial stability. It involves planning, organizing, and managing the financial activities of a company, including its capital structure, funding strategies, and investment decisions. Corporate finance professionals work closely with senior management to drive company growth while managing financial risks and optimizing the use of resources.
Corporate finance professionals are essential for making informed decisions about investments, managing risk, and ensuring that the company’s financial operations align with overall strategic goals. Whether a business is focused on expansion, acquisitions, or maintaining operations, corporate finance experts ensure that financial decisions support business objectives.
High-Paying Positions in Corporate Finance
Corporate finance includes several high-paying roles that cater to different aspects of a company’s financial health. Here are some of the top positions within this field:
- Chief Financial Officer (CFO): The CFO is responsible for the overall financial management of the company. They oversee all financial operations, including financial planning, risk management, and the creation of financial reports for stakeholders. They work directly with other C-suite executives to align financial strategies with company goals.
- Financial Controller: Financial controllers are responsible for ensuring that financial statements are accurate and compliant with accounting regulations. They also manage the company’s financial reporting and auditing processes, helping to maintain the integrity of financial records.
- Treasurer: A corporate treasurer focuses on managing the company’s financial assets and liabilities, as well as overseeing its capital structure. They are involved in securing funding, managing cash flow, and ensuring that the company has sufficient liquidity to meet its obligations.
Key Qualifications and Experience for Corporate Finance Roles
Succeeding in corporate finance requires a combination of technical finance knowledge, strategic thinking, and experience in managing large-scale financial operations. Some of the key qualifications and experiences required for success in this field include:
- Education: A strong background in finance, accounting, or economics is necessary. Many professionals in corporate finance hold an MBA, often specializing in finance, accounting, or strategic management. Additional certifications like CPA (Certified Public Accountant) or CFA (Chartered Financial Analyst) can be beneficial for certain roles.
- Experience: Corporate finance professionals typically have years of experience working in lower-level finance roles before advancing to senior positions like CFO. Experience in financial analysis, accounting, and budget management is critical.
- Analytical Skills: Corporate finance professionals need to have strong analytical abilities to assess financial reports, forecast trends, and make data-driven decisions that align with the company’s objectives.
- Leadership and Communication: Strong leadership skills are necessary for managing teams and collaborating with other executives. Excellent communication skills are essential for presenting financial strategies and reports to stakeholders and upper management.
Salary Ranges and Factors Affecting Compensation
Corporate finance offers competitive salaries, especially for senior-level positions. Compensation varies depending on the role, experience, company size, and geographic location. Here’s a breakdown of typical salary ranges:
- CFO: A Chief Financial Officer can earn a base salary of $150,000 to $400,000, with bonuses and profit-sharing potentially pushing total compensation above $1 million, depending on the company’s performance and size.
- Financial Controller: Financial controllers typically earn between $90,000 and $200,000 annually, with additional bonuses based on the company’s financial performance.
- Treasurer: Treasurers can expect base salaries ranging from $100,000 to $250,000 annually, with additional performance bonuses or stock options increasing total compensation.
Factors such as company size, industry, and geographic location will influence compensation. Larger companies or multinational corporations typically offer higher salaries and more generous bonus structures. Additionally, those in cities with a higher cost of living, such as New York or San Francisco, may see higher salaries.
Financial Planning and Wealth Management
Financial planning and wealth management have become increasingly important as individuals and families seek to grow and protect their wealth. As the financial landscape grows more complex, more people are turning to professionals who can provide tailored strategies for managing their investments, estate planning, retirement, and other financial goals.
The demand for skilled financial planners and wealth managers has surged in recent years, particularly among high-net-worth individuals, business owners, and families who want to ensure their financial futures. These professionals help clients optimize their investments, minimize tax burdens, and plan for future financial needs, offering advice that spans various areas of personal finance.
High-Paying Roles in Financial Planning and Wealth Management
The financial planning and wealth management sectors offer several high-paying positions, each with its own set of responsibilities:
- Financial Advisor: Financial advisors provide clients with advice on a range of financial topics, from investments to insurance and retirement planning. They help clients set and achieve their financial goals by recommending strategies tailored to their unique circumstances.
- Wealth Manager: Wealth managers serve high-net-worth individuals (HNWIs) or families and provide comprehensive financial services, including investment management, tax planning, estate planning, and philanthropic planning. They typically work with clients who have substantial assets and require customized financial strategies.
- Private Wealth Manager: These professionals work with ultra-high-net-worth individuals (UHNWIs), handling more complex financial needs. Private wealth managers manage all aspects of their clients’ wealth, including tax minimization, estate planning, charitable giving, and investment strategy.
- Certified Financial Planner (CFP): CFPs are professionals who hold a certification to offer comprehensive financial planning services. They focus on helping clients meet long-term financial goals and can offer advice on everything from investment planning to retirement and estate planning.
Skills Required for Success
To succeed in financial planning and wealth management, professionals need a mix of technical financial knowledge and strong interpersonal skills. Here are the most important skills for these roles:
- Analytical Skills: Wealth managers and financial planners need to be able to assess clients’ financial situations, analyze financial markets, and create tailored strategies that maximize returns while minimizing risk.
- Client Relationship Management: Building strong relationships with clients is essential. Financial advisors and wealth managers must listen to clients’ needs, provide ongoing support, and build trust to retain clients over time.
- Knowledge of Financial Products: A deep understanding of various financial products (stocks, bonds, mutual funds, retirement plans, insurance, etc.) is essential. These professionals must be able to recommend appropriate solutions based on clients’ financial goals.
- Regulatory Knowledge: Financial planners and wealth managers need to stay up-to-date with the latest regulatory changes that may affect their clients’ financial strategies. This includes tax laws, estate planning regulations, and investment policies.
- Certifications: Many professionals pursue certifications such as the Certified Financial Planner (CFP) designation to boost their credibility and expertise.
Salary Expectations and Compensation Structures
The financial planning and wealth management industry offers lucrative compensation, particularly for those with experience and a strong client base. Here’s a general breakdown of salary expectations:
- Financial Advisor: Financial advisors typically earn base salaries between $60,000 and $100,000 annually. However, their compensation often includes commissions and performance-based bonuses, pushing total earnings to $150,000 or more for experienced advisors.
- Wealth Manager: Wealth managers usually earn a base salary between $90,000 and $150,000 annually. With additional bonuses, commissions, and fees from clients, they can earn $300,000 or more annually.
- Private Wealth Manager: Private wealth managers can expect to earn salaries starting around $150,000, with total compensation potentially reaching $500,000 or more, depending on the size of their client base and the complexity of their work.
- Certified Financial Planner (CFP): Certified financial planners typically earn $80,000 to $150,000 annually, with experienced CFPs often earning six figures with the potential for significant bonuses.
Risk Management and Compliance
Risk management and compliance are critical areas within financial institutions, ensuring that companies operate within legal boundaries and manage potential risks effectively. As global markets become increasingly complex and interconnected, financial institutions are placing greater emphasis on identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks. This is crucial for maintaining stability, regulatory compliance, and business continuity.
Risk management and compliance professionals help financial institutions avoid financial losses, legal penalties, and reputational damage. These professionals also ensure that financial operations align with ever-changing local and international regulations, including anti-money laundering (AML), data protection, and financial crime laws.
High-Paying Roles in Risk Management and Compliance
The demand for skilled risk management and compliance professionals has grown in response to more stringent regulations and a higher risk of financial crises. Here are some of the high-paying roles in this sector:
- Risk Manager: Risk managers are responsible for identifying, analyzing, and mitigating risks that could affect the financial health of an organization. They use data-driven methods to assess risk exposure and develop strategies to minimize potential losses.
- Compliance Officer: Compliance officers ensure that a company complies with all financial regulations, including reporting requirements, anti-money laundering laws, and other industry-specific regulations. They help the company avoid legal issues and penalties by keeping operations compliant with the law.
- Chief Risk Officer (CRO): The CRO oversees the entire risk management strategy of an organization, working with other departments to identify and mitigate risks at every level of the business. They ensure that the company’s risk exposure is aligned with its business goals.
- Head of Compliance: These professionals lead a company’s compliance division, ensuring that the firm complies with external regulations and internal controls. They monitor new regulatory changes and adapt strategies to address them.
Qualifications Needed and Expertise Required
To succeed in risk management and compliance, you need a solid understanding of financial operations, strong analytical abilities, and in-depth knowledge of legal and regulatory frameworks. Here are some of the key qualifications:
- Education: A degree in finance, economics, law, or a related field is typically required. Advanced degrees like a Master’s in Finance, Economics, or an MBA can be advantageous.
- Certifications: Certifications such as the Financial Risk Manager (FRM), Certified Risk Manager (CRM), or Certified Regulatory Compliance Manager (CRCM) can enhance your credentials and help you advance in the field.
- Analytical Skills: Risk managers and compliance officers must be able to analyze complex data, identify potential risks, and design strategies to mitigate them.
- Regulatory Knowledge: A deep understanding of financial regulations, compliance standards, and industry best practices is essential for success in this field.
Salary Prospects and Job Growth
Risk management and compliance roles tend to offer competitive salaries, especially for senior positions. Here’s an overview of salary expectations:
- Risk Manager: Risk managers can expect to earn between $90,000 and $150,000 annually, with experienced professionals earning up to $200,000, especially in larger financial institutions.
- Compliance Officer: Compliance officers typically earn between $70,000 and $120,000 annually, with higher salaries in senior roles or large financial firms.
- Chief Risk Officer (CRO): CROs are some of the highest-paid professionals in the field, earning base salaries between $200,000 and $400,000, with bonuses and performance-based compensation driving total earnings to $500,000 or more.
- Head of Compliance: Heads of compliance can earn salaries between $150,000 and $300,000 annually, with additional performance-based bonuses.
Job growth in risk management and compliance is strong, driven by increasing regulatory requirements and the need for companies to manage complex financial risks. These roles are expected to remain in high demand, particularly as businesses continue to expand globally.
Quantitative Finance
Quantitative finance is a rapidly growing field within the finance industry, combining mathematics, statistics, and programming to analyze and manage financial markets. This field has become essential in recent years, as financial institutions increasingly rely on quantitative models to drive decision-making, assess risk, and predict market movements. Professionals in quantitative finance, also known as “quants,” use advanced mathematical and statistical techniques to develop models and algorithms that can process vast amounts of data to forecast market trends and optimize investment strategies.
Quantitative finance has applications in investment banks, hedge funds, asset management, and proprietary trading firms, where professionals develop and use complex algorithms to maximize returns and minimize risk.
High-Paying Roles in Quantitative Finance
Quantitative finance offers some of the most lucrative career paths in finance. The following roles are among the highest-paying positions within the field:
- Quantitative Analyst (Quant): Quantitative analysts develop mathematical models to analyze financial markets and optimize investment strategies. They are highly skilled in programming, statistics, and finance. Quants work in hedge funds, investment banks, and trading firms, developing algorithms that help traders make decisions.
- Financial Engineer: Financial engineers design and implement models to manage financial risk, optimize investments, and price complex financial instruments. They often work on derivative pricing, risk management strategies, and portfolio optimization.
- Quantitative Trader: Quantitative traders use quantitative models to guide trading decisions. They analyze data, develop strategies, and execute trades at high speeds. These traders typically use algorithms and automated trading systems to maximize profits while minimizing risk.
- Data Scientist in Finance: While not traditionally associated with finance, data scientists are increasingly sought after to apply machine learning and big data analytics to financial decision-making. Their role involves analyzing massive datasets and creating predictive models that guide investment strategies.
Key Skills and Knowledge Areas Needed
To succeed in quantitative finance, professionals need expertise in a combination of finance, mathematics, and technology. Some key skills and knowledge areas include:
- Mathematics and Statistics: A deep understanding of mathematical and statistical concepts is essential. Professionals should be skilled in calculus, linear algebra, probability, and stochastic processes.
- Programming: Proficiency in programming languages like Python, C++, Java, and R is crucial for developing algorithms and financial models.
- Finance: A strong understanding of financial markets, instruments, and risk management techniques is necessary to apply mathematical models effectively.
- Machine Learning and Data Analytics: As the use of artificial intelligence grows, skills in machine learning and big data analytics are becoming increasingly valuable in quantitative finance.
Salary Potential and Growth Opportunities
Quantitative finance is known for offering some of the highest salaries in the financial industry. Here’s a breakdown of salary expectations:
- Quantitative Analyst: Junior quants typically earn between $100,000 and $150,000 annually. Senior quants or those at top hedge funds can earn well over $300,000 per year, including bonuses.
- Financial Engineer: Financial engineers can expect base salaries of $120,000 to $200,000, with the potential for significant bonuses tied to the performance of their models.
- Quantitative Trader: Quantitative traders can earn between $150,000 and $300,000 in base salary, with bonuses pushing total compensation to $500,000 or more, depending on their performance.
- Data Scientist in Finance: Data scientists in finance typically earn salaries ranging from $120,000 to $200,000 annually, with the potential for bonuses based on their ability to create valuable insights from data.
As financial institutions continue to adopt more advanced quantitative methods, job growth in this field is expected to remain strong, with quants and financial engineers in high demand. The potential for career advancement is also significant, with top professionals earning seven-figure salaries.
Conclusion
The finance industry offers a wide variety of high-paying careers, each catering to different skills and interests. Whether you’re drawn to analyzing markets, managing risks, or helping individuals grow their wealth, there’s a role that can match your strengths and financial goals. These jobs not only offer competitive base salaries but also often come with bonuses, stock options, and performance-based rewards that can significantly increase total compensation. With the demand for financial professionals continuing to grow, you’ll find plenty of opportunities to advance your career and increase your earning potential over time.
While the path to these top-paying roles in finance may require a mix of education, specialized skills, and experience, the rewards can be well worth the effort. Whether you’re interested in high-stakes environments like investment banking and hedge funds, or you prefer roles in wealth management and risk assessment, there are plenty of avenues to explore. Understanding the financial expectations, key qualifications, and responsibilities for each role will help you target the best opportunities and set yourself up for success in one of the most lucrative industries.
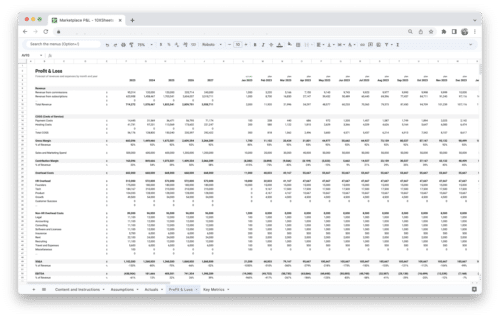
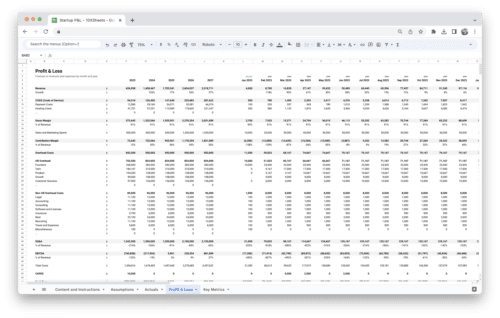
Get Started With a Prebuilt Template!
Looking to streamline your business financial modeling process with a prebuilt customizable template? Say goodbye to the hassle of building a financial model from scratch and get started right away with one of our premium templates.
- Save time with no need to create a financial model from scratch.
- Reduce errors with prebuilt formulas and calculations.
- Customize to your needs by adding/deleting sections and adjusting formulas.
- Automatically calculate key metrics for valuable insights.
- Make informed decisions about your strategy and goals with a clear picture of your business performance and financial health.